Thailand Medical Study Shows That Certain Thai Traditional Medicines Reduce CD147 Levels In Lung Cells. Possible Use In Cancers And COVID-19!
Kittisak Meepoon Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Mar 16, 2024 1 year, 11 months, 1 week, 5 days, 5 hours, 26 minutes ago
Thailand Medical: In a groundbreaking study conducted by the Faculty of Science at Nakhon Phanom University, the Center for Research and Development of Herbal Health Products at Khon Kaen University, and the Thai Traditional and Alternative Medicine department at Nakhon Phanom Hospital in Thailand, a new frontier in traditional medicine has been unveiled. The study sheds light on the potential of certain Thai traditional medicines (TTMs) in reducing CD147 levels in lung cells, thereby opening avenues for their use in treating various conditions including cancers, inflammations, and COVID-19.
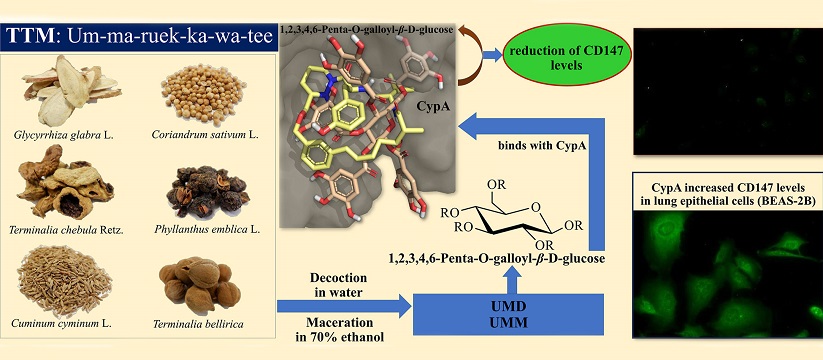 Graphical Abstract - Thai Traditional Medicines Reduce CD147 Levels In Lung Cells. Possible Use In Treating Cancers, Inflammation And COVID-19
Understanding CD147 and its Implications
Graphical Abstract - Thai Traditional Medicines Reduce CD147 Levels In Lung Cells. Possible Use In Treating Cancers, Inflammation And COVID-19
Understanding CD147 and its Implications
CD147, also known as basigin or EMMPRIN, is a pivotal signaling protein implicated in a range of diseases such as cancers, inflammations, and COVID-19. Its interaction with extracellular cyclophilin A (CypA) is a crucial mechanism driving inflammation and disease progression. Elevated CD147 levels are associated with a heightened inflammatory response and disease severity, making it a prime target for therapeutic intervention.
The Role of Thai Traditional Medicines
Thai traditional medicines, deeply rooted in centuries-old wisdom, have long been used to treat various ailments. It stills a role in modern day healthcare with many
Thailand Medical institutions such as hospitals and universities having departments dedicated to its use and study.
Four herbal formulas - Keaw-hom (KH), Um-ma-ruek-ka-wa-tee (UM), Chan-ta-lee-la (CT), and Ha-rak (HR) - have particularly stood out for their anti-pyretic and anti-respiratory properties. These medicines have been included in Thailand's National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) due to their efficacy and safety.
The Study's Objectives
The primary objective of the study was to explore the effects of KH, UM, CT, and HR on reducing CD147 levels, with a specific focus on lung cells. By leveraging both in vitro and in silico methodologies, the researchers aimed to identify active compounds within these traditional medicines that could modulate CD147 expression.
Methodology
The study employed advanced techniques such as immunofluorescent assays to assess CD147 levels in human lung epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) stimulated with CypA. Eight extracts from KH, UM, CT, and HR were analyzed, including those derived from water decoction (D) and 70% ethanol maceration (M). The analysis focused on identifying the most effective extracts and their chemical constituents responsible for CD147 reduction.
Key Findings
Among the herbal extracts tested, UM exhibited the most significant efficacy in reducing CD147 levels in lung cells. Phenolic compounds, particularly polyphenols, polyphenol sugars, and flavon
oids, were identified as major contributors to UM's therapeutic effects. Molecular docking studies further elucidated the role of polyphenol sugars as potent CypA inhibitors, providing mechanistic insights into UM's mode of action.
Implications and Future Directions
The findings from this study hold immense promise for the development of UM as a potential therapeutic agent against CD147-associated diseases. Given the broad spectrum of conditions linked to CD147 dysregulation, including cancers, inflammations, and COVID-19, UM and similar TTMs could emerge as valuable additions to modern medical interventions.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While this study marks a significant milestone, further research is warranted to fully harness the therapeutic potential of TTMs. Clinical trials and translational studies are essential to validate these findings in real-world settings. Collaboration between traditional medicine practitioners, scientists, and healthcare professionals will be instrumental in bridging the gap between traditional wisdom and modern healthcare needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Thailand's pioneering research in traditional medicine underscores the rich heritage and untapped potential of TTMs in addressing complex diseases. The ability of UM to reduce CD147 levels signifies a promising avenue for combating CD147-associated diseases, offering new hope to patients worldwide. As we embark on this journey of discovery and validation, the fusion of traditional knowledge with scientific rigor paves the way for transformative advancements in healthcare. Thailand's medical community stands poised to lead this transformative charge, unlocking the healing powers of nature's remedies for the benefit of humanity.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Ethnopharmacology.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874124003416
For the latest
on Thai Herbal Medicine, keep on logging to
Thailand Medical News
