Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 28, 2024 1 year, 2 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 16 hours, 45 minutes ago
Medical News: Understanding Influenza A Virus Challenges
Influenza A virus (IAV) remains a significant global health challenge due to its ability to cause pandemics and seasonal epidemics. Despite advancements in virology, the virus continues to evade immune responses, leading to severe health consequences for vulnerable populations. Researchers from Tianjin University in China have shed light on a novel mechanism employed by IAV to suppress the immune response, potentially paving the way for targeted therapies. This
Medical News report explores their groundbreaking findings.
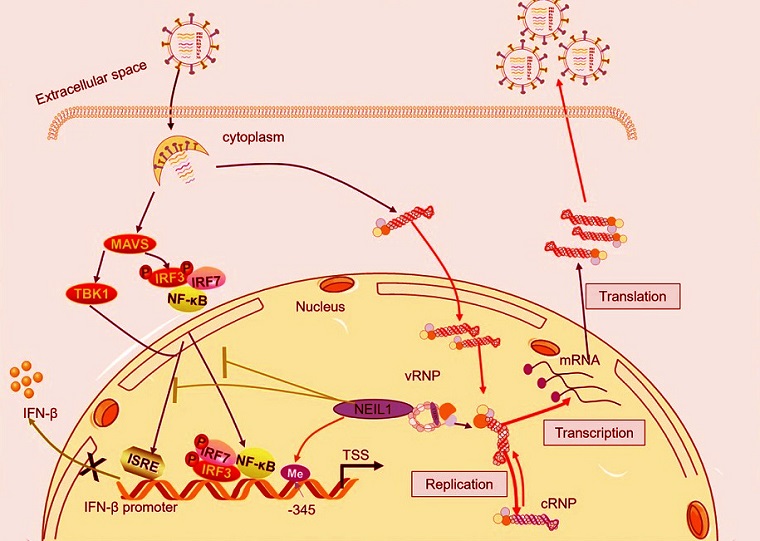 Mechanisms of NEIL1 promoting IAV proliferation.The schematic model of NEIL1 enhances IAV replication and suppresses the expression of IFN-β. NEIL1 facilitates the nuclear entry of the vRNP complex and its replicative transcriptional activity within the nucleus through interactions with NP proteins, thereby promoting the proliferation of IAV. In addition, NEIL1 is a key effector molecule that negatively regulates IFN-β production and modulates IFN-β expression by regulating the methylation status of multiple sites in the IFN-β promoter region in the nucleus, in particular the GC site located at position −345 upstream of the transcription start site (CpG-345).
Discovering NEIL1’s Role
Mechanisms of NEIL1 promoting IAV proliferation.The schematic model of NEIL1 enhances IAV replication and suppresses the expression of IFN-β. NEIL1 facilitates the nuclear entry of the vRNP complex and its replicative transcriptional activity within the nucleus through interactions with NP proteins, thereby promoting the proliferation of IAV. In addition, NEIL1 is a key effector molecule that negatively regulates IFN-β production and modulates IFN-β expression by regulating the methylation status of multiple sites in the IFN-β promoter region in the nucleus, in particular the GC site located at position −345 upstream of the transcription start site (CpG-345).
Discovering NEIL1’s Role
Through high-throughput screening of epigenetic modifiers, the researchers identified a key protein, NEIL1 (nei endonuclease VIII-like 1), as a critical factor in IAV’s strategy to suppress immune responses. NEIL1, primarily recognized for its role in DNA repair, was found to interfere with the production of interferon-beta (IFN-β), a vital component of the innate immune response. By suppressing IFN-β, NEIL1 aids the virus in evading the immune system and promotes its replication.
The study revealed the interaction between NEIL1 and the IAV nucleoprotein (NP). This interaction facilitates the entry of NP into the host cell nucleus, stabilizing the viral ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) complex. The vRNP complex is crucial for the virus's replication and transcription processes, underscoring NEIL1’s significant role in enhancing IAV proliferation.
Understanding the Mechanism
The researchers employed various advanced techniques, including CRISPR-Cas9-based screening, gene expression analyses, and immunoprecipitation assays, to uncover the mechanisms by which NEIL1 influences IFN-β production. Key findings include:
-Epigenetic Regulation of IFN-β: NEIL1 alters the methylation of specific sites on the IFN-β promoter, particularly CpG-345, inhibiting its expression. This methylation-based regulation is independent of NEIL1’s enzymatic activity, highlighting a novel, enzyme-independent role of this protein.
-Suppression of Downstream Genes:
Beyond IFN-β, NEIL1 also suppresses the expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) like MX1, OAS1, and CCL5. These genes play crucial roles in antiviral defense, and their suppression creates a favorable environment for the virus to replicate.
-Facilitation of Viral Replication: NEIL1’s interaction with IAV NP enhances the stability and nuclear localization of the vRNP complex, directly boosting the virus’s ability to replicate and transcribe its genome.
-Selective Interaction with Influenza A: Interestingly, NEIL1 was found to interact exclusively with NPs of influenza A viruses but not influenza B viruses. This specificity highlights potential avenues for developing targeted treatments against influenza A.
Significance and Potential Applications
The study provides critical insights into the dual role of NEIL1 as a regulator of immune responses and a promoter of viral replication. By uncovering the mechanisms by which NEIL1 modulates host immunity and supports viral proliferation, the research opens doors to novel therapeutic strategies. Targeting NEIL1 or its interaction with IAV NP could offer new ways to combat influenza A infections, particularly those caused by highly pathogenic strains.
Conclusions and Implications
This study underscores the complex interplay between host and viral factors in determining the outcome of infections. NEIL1 emerges as a pivotal player in this interaction, simultaneously undermining the immune response and promoting viral survival. These findings not only enhance our understanding of IAV pathogenesis but also highlight the potential of NEIL1 as a target for antiviral therapy.
The implications of this research extend beyond influenza, as similar mechanisms may be employed by other RNA viruses. By focusing on epigenetic and enzyme-independent pathways, scientists can explore innovative approaches to bolster immune defenses against a wide range of pathogens.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: npj Viruses.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-024-00065-x
For the latest Influenza News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/ubiquitin-proteasome-system-as-a-new-target-to-fight-influenza-a-virus
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/soybean-extract-shows-promise-in-inhibiting-influenza-virus-entry
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/chinese-scientists-warn-of-new-h2n2-influenza-strain-that-could-be-a-human-pandemic-threat
