COVID-19 News: Study Shows That SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 Plays Key Roles In Interferon Antagonism And Viral Pathogenesis
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Sep 26, 2023 2 years, 4 months, 2 weeks, 3 days, 18 hours, 16 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: In the battle against the COVID-19 pandemic, understanding the intricacies of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its interactions with the host immune system is paramount. Recent research conducted at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York-USA, has shed light on a crucial player in this viral drama: ORF6, an accessory protein encoded by SARS-CoV-2. This
COVID-19 News coverage of the study delves into the multifaceted role of ORF6, uncovering its ability to antagonize interferon (IFN) responses, manipulate nucleocytoplasmic trafficking, and contribute to viral pathogenesis. Moreover, the research highlights the impact of a specific ORF6 variant polymorphism, D61L, found in the Omicron BA.2 and BA.4 variants. These findings deepen our understanding of SARS-CoV-2's immune evasion strategies and its consequences for viral pathogenesis.
 Graphical Abstract
The Ongoing Challenge of COVID-19
Graphical Abstract
The Ongoing Challenge of COVID-19
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to affect lives worldwide, it remains a significant global health concern. The disease's clinical spectrum ranges from asymptomatic cases to severe illness, with an overall fatality rate hovering around 1%. While various factors contribute to disease severity, mounting evidence suggests that a robust and timely antiviral interferon (IFN) response is critical for controlling SARS-CoV-2 infection. Individuals with impaired IFN pathways or autoantibodies against type I IFN are more susceptible to severe COVID-19. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 has evolved an array of mechanisms to counteract host immune defenses, emphasizing the pivotal role of IFN in combatting the virus.
A Glimpse into SARS-CoV-2's Immune Evasion Arsenal
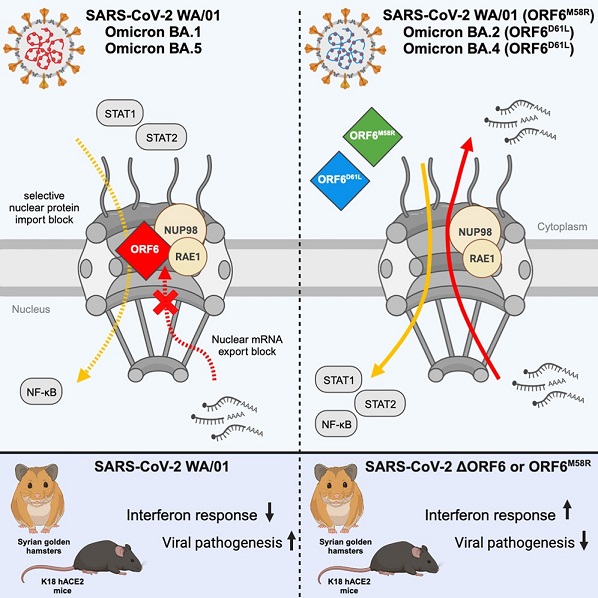
SARS-CoV-2 employs a repertoire of viral proteins to suppress or subvert the host's innate immune response. Among these proteins, ORF6 has emerged as a key player. ORF6's role in immune evasion centers around its interaction with the nuclear pore complex component Nup98-Rae1, which has significant implications for nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. Specifically, ORF6 interferes with the nuclear import of essential transcription factors, such as IRF and STAT proteins, pivotal players in the IFN response. This disruption of nuclear import hinders the host's ability to activate critical antiviral genes.
Additionally, ORF6 disrupts mRNA nuclear export, leading to a profound remodeling of the host cell's proteome. By doing so, ORF6 indirectly influences viral protein expression, further tipping the balance in favor of the virus. These mechanisms collectively underscore the significance of ORF6 in antagonizing innate immunity and orchestrating SARS-CoV-2&am
p;#39;s strategy for evading the host's defense mechanisms.
The Omicron Variant and ORF6: A Complex Relationship
As SARS-CoV-2 has evolved, new variants have arisen with substantial genomic changes that impact its virulence and transmissibility. Intriguingly, these variants often carry mutations affecting viral proteins involved in innate immune antagonism, including ORF6. This study hones in on the Omicron variants, BA.2 and BA.4, both of which harbor the ORF6:D61L mutation. This specific mutation has significant consequences as it disrupts ORF6's interactions with Nup98-Rae1, thereby impairing its ability to evade the host immune system.
In-Depth Analysis of ORF6's Functions
To unravel the intricate web of ORF6's functions, the research conducted experiments using recombinant viruses carrying deletions or loss-of-function mutations in ORF6. These experiments yielded several key findings:
-ORF6's Role in STAT Nuclear Import: ORF6 is pivotal in inhibiting STAT1/2 nuclear translocation during infection, effectively suppressing the expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). This inhibition was observed both in vitro and in a Syrian golden hamster model.
-Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Import: ORF6 selectively blocks karyopherin-mediated nuclear import pathways, affecting specific transcription factors while sparing others, such as NF-κB p65. This selectivity suggests the existence of distinct cargo complexes dependent on Nup98.
-Interference with mRNA Nuclear Export: ORF6 disrupts Nup98-Rae1 mRNA export functions, contributing to the host's decreased protein synthesis during infection. The Omicron variant's ORF6:D61L mutation further accentuates this effect, impacting viral transmissibility and pathogenicity.
-Implications for Viral Pathogenicity: ORF6's contribution to viral pathogenesis was evident in experiments involving Syrian golden hamsters and K18 human ACE2 mice. Animals infected with ORF6-deficient viruses experienced reduced lung injury and enhanced ISG expression, reflecting the protein's role in SARS-CoV-2 virulence.
-Modulation of Viral Protein Expression: Surprisingly, ORF6 was found to influence the relative expression of various viral proteins, favoring structural and accessory genes. The exact mechanism underlying this phenomenon requires further investigation, but it highlights the multifaceted role of ORF6 in viral pathogenesis.
Concluding Thoughts
This comprehensive study delves into the critical role of SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 in immune evasion and viral pathogenesis. The findings underscore ORF6's ability to disrupt nucleocytoplasmic trafficking, inhibit host gene expression, and modulate viral protein production. Moreover, the study illuminates the impact of the ORF6:D61L mutation, found in Omicron variants, on the virus's ability to evade host immune responses.
Understanding these intricate mechanisms is essential for developing effective strategies to combat SARS-CoV-2 and its evolving variants. It highlights the need for ongoing genomic surveillance and variant analysis to stay ahead of the virus's adaptive strategies. As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to challenge global health, this research brings us one step closer to deciphering the virus's secrets and devising effective countermeasures.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: cell Host and Microbe.
https://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(23)00328-1
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
