Viruses Use Short Sequence Motifs To Subvert PDZ Domain Mediated Host Cell Polarity Signaling. SARS-CoV-2 Does This Using The E Proteins!
SARS-CoV-2-Research - Short Sequence Motifs - PDZ Domain - Host Cell Polarity Signaling Jul 19, 2023 2 years, 6 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 14 hours, 19 minutes ago
Understanding How SARS-CoV-2 Also Indulges In Manipulating Cell Polarity Signaling Using E proteins Will Give Us Better Insights Into Its Pathogenesis
SARS-CoV-2 Research: Cell polarity, the asymmetrical distribution of molecules within a cell, is crucial for proper tissue development and function. It guides essential cellular processes such as cell division, migration, and neuronal signaling.
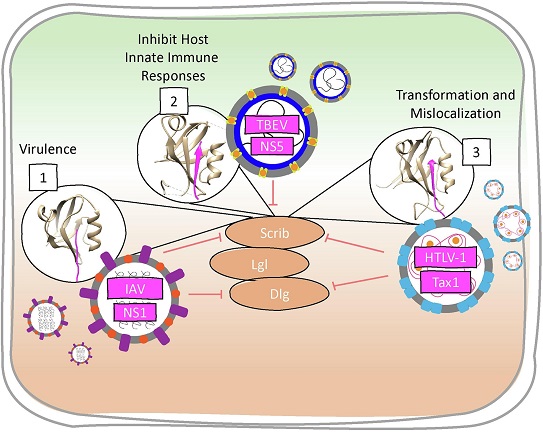 General representation of PDZ domains controlling signaling pathways involved
General representation of PDZ domains controlling signaling pathways involved
in viral infection. Amino acid differences in IAV NS1 PBM sequences influence
viral virulence. TBEV NS5 PBM binds to SCRIB PDZ3 to disrupt interferon
facilitated JAK/STAT signaling, seemingly to evade the innate immune responses.
HTLV-1 Tax1 PBM is important for T-cell transformation and binds to all SCRIB
PDZ domains to cause mislocalization
However, viruses have evolved strategies to manipulate cell polarity signaling for their benefit, leading to dysregulation and potential health consequences.
Researchers from La Trobe University and the University of Melbourne in Australia are delving into the mechanisms through which viral effector proteins disrupt host cell polarity signaling, shedding light on potential therapeutic interventions and advancing our understanding of tissue homeostasis.
Unraveling Cell Polarity
Cell polarity can take various forms, including asymmetric cell division, planar cell polarity, apical-basal cell polarity, and front-rear cell polarity. These different types of polarity rely on the interplay of protein complexes such as the PAR complex, Crumbs complex, and SCRIB complex. These complexes regulate the distribution of biomolecules within cells, ensuring proper orientation and function.
Viral Exploitation of Cell Polarity
Numerous viruses have been found to target cell polarity regulators, using their effector proteins to interfere with the function of essential proteins featuring PDZ domains. PDZ (PSD-95, DLG, and ZO-1) domains are protein interaction modules that bind to specific sequence motifs known as PDZ-binding motifs (PBM). Viruses such as papillomaviruses, flaviviruses, and coronaviruses have developed effector proteins that outcompete or misdirect host polarity regulators, enabling viral spread, enhanced infectivity, or even virus-induced tumorigenesis.
Deciphering the Viral Strategy
PDZ domains play a critical role in cellular signaling, mediating interactions between membrane proteins and intracellular signaling partners. Viruses exploit these interactions to their advantage. However, achieving selectivity for specific PDZ domains poses a challenge for therapeutic interventions. PDZ domains are promiscuous, binding to multiple partners, and the precise classification of PDZ-binding motifs is still under investigation. Nonetheless, understanding the direct protein-protein interactions utilized by viral effector proteins will provide insights into their mechanisms of action and potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Coronaviruses and Cell Polarity
t;
Coronaviruses, responsible for respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases, have also been found to exploit cell polarity. The E protein of coronaviruses interacts with polarity-related proteins, disrupting the architecture of epithelial cells. For example, the SARS-CoV-1 E protein binds to the polarity protein PALS1, leading to the inhibition of PALS1 and the disruption of tight junctions. This interaction alters cellular morphology and facilitates viral infiltration into underlying tissues. Similar mechanisms may be at play in SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV infections and further
SARS-CoV-2 Research is warranted in this area.
Implications and Future Directions
The manipulation of cell polarity by viruses has broad implications for viral pathogenesis and potential therapeutic interventions. Understanding the intricate interactions between viral effectors and host cell polarity regulators can guide the development of targeted therapies. One promising approach is the design of peptide inhibitors that disrupt PDZ-PBM interactions. However, achieving selectivity and efficacy remains a challenge.
Concluding Thoughts
The study of viral manipulation of cell polarity signaling provides a unique window into the complex world of polarity regulation and its role in various diseases.
Viruses exploit cell polarity to facilitate their replication, evade the host immune response, and promote viral pathogenesis. By unraveling the interactions between viral effectors and host cell polarity regulators, researchers can pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies and deepen our understanding of fundamental biological processes.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular Cell Research (Science Direct).
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167488923001088
For the latest on
SARS-CoV-2 Research, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
