COVID-19 news - IL-10 Jun 08, 2023 2 years, 8 months, 5 days, 22 hours, 24 minutes ago
Understanding The Dualistic Role Of Interleukin 10 In COVID-19.
COVID-19 News: IL-10, a versatile cytokine involved in regulating inflammation and maintaining immune balance, plays a significant role in COVID-19 and post-COVID conditions according to a new research by Italian researchers. IL-10 acts as an anti-inflammatory molecule, protecting against excessive immune responses.
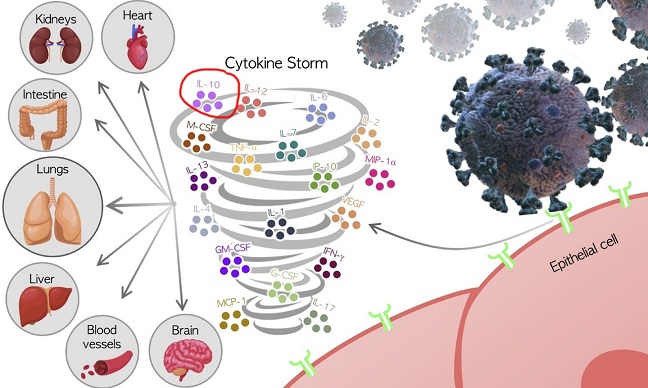
In COVID-19, IL-10 is released as a danger signal by damaged tissues to prevent harmful hyperinflammation. Monitoring IL-10 levels could serve as a predictor of disease severity and mortality. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance IL-10's immunomodulatory actions to counteract cytokine storms and mitigate complications.
Cytokines are small proteins that facilitate communication between cells and regulate immune responses. They act locally or systemically and bind to specific receptors on target cells, initiating signaling cascades. Cytokines play crucial roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and immune regulation.
Dysregulation of cytokines is implicated in various diseases, including COVID-19.The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a dysregulated immune response characterized by a cytokine storm. Severe cases of COVID-19 are associated with excessive pro-inflammatory cytokine release, triggering an inflammatory response that leads to organ failure and death.
Furthermore, a significant percentage of individuals experience persistent symptoms after the acute infection, known as "long COVID" or "post-COVID-19 syndrome." The underlying molecular mechanisms and potential therapies for these post-COVID conditions are still under investigation.
IL-10 is a cytokine that maintains immune system homeostasis. It binds to specific receptors, initiating signaling pathways that regulate gene expression. IL-10 exhibits anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, but it can also stimulate immune responses. It is produced by various cell types and has pleiotropic effects on the immune system. IL-10 is involved in other biological processes, such as nervous system homeostasis and wound repair. Dysregulation of IL-10 is associated with autoimmune diseases and cancer.
COVID-19 is characterized by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which is a severe complication affecting a significant percentage of patients admitted to intensive care units. ARDS is marked by respiratory insufficiency, pulmonary damage, and a dysregulated immune response that can lead to multiple organ failure and mortality. In the context of COVID-19, alveolar epithelial cells, alveolar macrophages, and dendritic cells play critical roles as sensors of the respiratory mucosa, triggering an immune response upon SARS-CoV-2 infection. This response involves the release of various pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, resulting in the recruitment and activation of immune cells.
While the host immune response is necessary to combat the infection, an excessive and uncontrolled inflammatory response can lead to tissue damage and a cascade of detrimental effects throughout the body. Several pro-inflammatory molecules have been implicated in this cytokine storm, including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and IFN-γ. Notably, COVID-19 patients wi
th severe forms of the disease exhibit significantly elevated levels of IL-10, a unique characteristic distinguishing SARS-CoV-2 infections from other beta-coronaviruses as covered in previous studies and also past
COVID-19 News coverages.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-latest-study-shows-sars-cov-2-impairs-immune-system-including-causing-t-cell-lymphopenia-but-increases-il%E2%80%9010%E2%80%90producing-regulatory-t-cells
Studies have shown that IL-10 plays a dual role in COVID-19, depending on the timing and magnitude of its secretion. In the early stages of infection, IL-10 may act as a negative feedback mechanism, counterbalancing the excessive pro-inflammatory response and protecting against tissue damage. However, in later phases, sustained and elevated IL-10 production can exacerbate the inflammatory response, leading to disease progression.
The increased levels of IL-10 in severe COVID-19 cases have raised questions about its immunosuppressive action and its potential resistance in the face of overwhelming inflammation. Some evidence suggests that immune cells may become hypo-responsive to the immunosuppressive effects of IL-10, leading to uncontrolled release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This resistance to IL-10 has been observed in patients with type 2 diabetes, who are at a higher risk of severe complications from COVID-19. Restoring responsiveness to IL-10 through pharmacological interventions could be a promising therapeutic strategy to alleviate inflammation in severe COVID-19 patients, particularly those with diabetes.
In addition to its role in COVID-19, IL-10 has also been implicated in post-COVID conditions, where patients experience persistent symptoms for an extended period after the initial infection. The symptoms of post-COVID syndrome are highly diverse and can affect various systems in the body. Fatigue, respiratory problems, pain, neurological issues, and psychological symptoms are among the common manifestations. IL-10 may contribute to the development of these symptoms, and its elevated levels have been associated with disease severity and poor outcomes.
However, studies have also shown that IL-10 treatment can reduce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulate immune responses, making it a potential therapeutic target for various diseases.
In the context of autoimmune diseases, IL-10 has been studied for its immunosuppressive effects. It can dampen the immune response by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). By reducing the levels of these cytokines, IL-10 helps to attenuate the inflammatory process and limit tissue damage.
In animal models and early clinical trials, IL-10 has shown promise in the treatment of diseases such as Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. However, further research is still needed to fully understand its therapeutic potential and optimize its clinical application.
In addition to autoimmune diseases, IL-10 has also been implicated in other conditions, including certain types of cancer. In some cases, IL-10 can promote tumor growth and immune evasion by suppressing the immune response against cancer cells. However, in other instances, IL-10 can have anti-tumor effects by enhancing immune surveillance and promoting the activity of certain immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells.
Monitoring IL-10 levels in patients can provide valuable information about disease progression and response to treatment. Low levels of IL-10 may indicate a dysregulated immune response and increased disease activity, while high levels of IL-10 could suggest a more regulated immune response or a therapeutic response to IL-10 treatment.
IL-10 has shown promise as a reliable predictor of COVID-19 severity and outcome, as well as a potential target for counteracting hyperinflammation during both the acute infection and post-infection phases.
In summary, IL-10 plays a critical role in COVID-19 and post-COVID conditions by regulating immune responses and preventing excessive inflammation. Monitoring IL-10 levels could aid in predicting disease severity and mortality. Enhancing IL-10's immunomodulatory actions and exploring natural compounds that increase IL-10 expression hold promise for managing inflammation. Understanding the structure and signaling pathways of IL-10 provides insights into its therapeutic potential and immune regulatory functions. Further research is needed to explore the administration of exogenous IL-10 or adjuvants that activate anti-inflammatory IL-10 signaling as potential therapeutic strategies for improving COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 symptoms.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers In Immunology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161067/full
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
