South Korean Study Finds That COVID-19 Vaccines Linked to Higher Risk of Respiratory Illnesses!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 17, 2025 3 months, 1 week, 1 day, 1 hour, 39 minutes ago
Medical News: Rising Concerns Over New Respiratory Infection Trends as a Result of the COVID-19 Vaccines!
A major nationwide study from South Korea has raised new questions about how repeated COVID-19 vaccination may influence susceptibility to other respiratory infections in the post-pandemic era. The research team, involving experts from Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, and Seoul National University, analyzed health records from all 51.6 million people across the country. Their findings show clear shifts in infection patterns and a troubling rise in certain illnesses among individuals who received four or more vaccine doses. According to this
Medical News report, the trends highlight unexpected vulnerabilities that emerged as society transitioned into the “Post-COVID” phase.
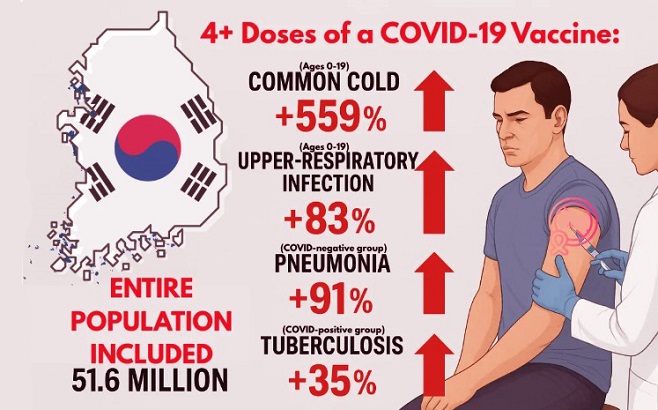 New nationwide data from South Korea links higher COVID-19 vaccine dose numbers to rising rates of respiratory infections in the post-pandemic era
Understanding the Nationwide Data
New nationwide data from South Korea links higher COVID-19 vaccine dose numbers to rising rates of respiratory infections in the post-pandemic era
Understanding the Nationwide Data
The study evaluated vaccination records and insurance-based disease diagnoses between June 2023 and September 2024. Researchers found that while influenza-like illnesses dropped dramatically during the pandemic due to mask use, distancing, and reduced circulation of respiratory viruses, conditions such as the common cold, upper-respiratory tract infections (URI), tuberculosis, and pneumonia rebounded sharply in 2023 and 2024. The most significant discovery was a strong dose-dependent pattern: the more COVID-19 vaccine doses a person received, the higher their risk of developing common respiratory infections.
Children and teenagers showed the steepest increases, with those receiving four or more doses experiencing up to 559 percent higher risk of the common cold.
Respiratory Risks Rise Steadily with Each Additional Dose
For upper-respiratory tract infections, children who received four or more doses saw an 83 percent higher risk, while older adults experienced a 57 percent increase. Pneumonia rates rose as well, especially among COVID-negative individuals, with those receiving four or more doses showing a 91 percent higher risk. Tuberculosis risk also increased among people who had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2. Even pooled models covering the entire population revealed strong upward trends for common colds and URI with every additional dose. These findings persisted even after adjusting for age, prior infections, comorbidities, and income levels.
Why Are These Patterns Emerging Now
Researchers believe a combination of factors may be driving these results. Immune exhaustion following repeated exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or vaccination, reduced natural exposure to common pathogens during the pandemic years, and changes in population-level immunity may all play a role. The study also notes that influenza-like illness and pertussis appeared lower among heavily vaccinated individuals, but these reductions may reflect diagnostic biases and coding changes rather than true protection. Meanwhile, pertussis ca
ses nationwide surged 46-fold in 2023, contradicting any apparent protection seen in adjusted models.
Conclusions
This large-scale study reveals a complex and changing landscape of respiratory infections in the post-COVID world. While some respiratory illnesses appeared reduced, the strong, consistent, and dose-dependent rise in common colds, upper-respiratory infections, pneumonia, and tuberculosis among individuals with four or more vaccine doses raises critical questions about long-term immune responses. The conclusions point toward an urgent need for deeper investigation into immune system changes following repeated mRNA vaccination and SARS-CoV-2 infection. The findings underscore that public health strategies must now focus not only on COVID-19 itself but on the wider impact that pandemic-era immunity shifts and vaccine exposures may have created. Understanding these patterns will be central to preparing for future seasonal outbreaks and protecting vulnerable age groups, especially children and older adults who showed the strongest responses in this study.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed International Journal of Infectious Diseases
https://www.ijidonline.com/article/S1201-9712(25)00416-3/fulltext
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/vaccine-news
