BREAKING! French Study Shows That SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein (E) Binds And Activates TLR2 And Causes Production Of CXCL8 Inflammatory Chemokine!
Source: Medical News-SARS-CoV-2 Research Nov 14, 2021 4 years, 3 months, 1 week, 3 days, 15 hours, 32 minutes ago
SARS-CoV-2 Research: A new study by French researchers from INSERM, CNRS and Université Paul Sabatier along with scientific support from the University of California Irvine-USA have discovered that the SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein (E) binds and activates TLR2 and causes production of CXCL8 inflammatory chemokine.
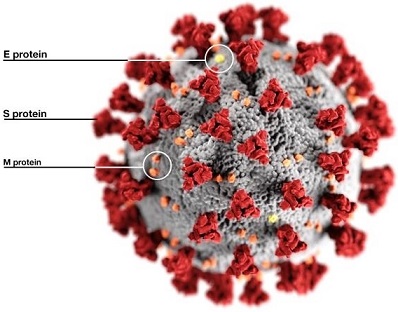
The study findings show that the often-ignored SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein (E) is a critical target for COVID-19 interventions.
Toll-like receptor 2 also known as TLR2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR2 gene. TLR2 has also been designated as CD282 (cluster of differentiation 282). TLR2 is one of the toll-like receptors and plays a role in the immune system. TLR2 is a membrane protein, a receptor, which is expressed on the surface of certain cells and recognizes foreign substances and passes on appropriate signals to the cells of the immune system.
The
SARS-CoV-2 Research team presented a molecular characterization of the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein E with TLR2.
The team demonstrated that E protein interacts physically with TLR2 receptor in a specific and dose-dependent manner.
Furthermore, the study findings showed that this interaction is able to engage TLR2 pathway as demonstrated by its capacity to activate NF-κB transcription factor and to stimulate the production of CXCL8 inflammatory chemokine in a TLR2-dependent manner.
In addition, in agreement with the importance of NF-κB in TLR signaling pathway, the study findings showed that the chemical inhibition of this transcription factor led to significant inhibition of CXCL8 production, while blockade of P38 and ERK1/2 MAP kinases resulted only in a partial CXCL8 inhibition.
The study findings suggest considering the envelope protein E as a novel target for COVID-19 interventions: (i) either by exploring the therapeutic effect of anti-E blocking/neutralizing antibodies in symptomatic COVID-19 patients, or (ii) as a promising non-Spike SARS-CoV-2 antigen candidate to include in the development of next generation prophylactic vaccines against COVID-19 infection and disease.
The study findings were published on a preprint server and are currently being peer reviewed.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.11.10.468173v1
Though, the exact mechanisms of COVID-19 pathogenesis are unknown, recent data demonstrated that elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum is associated with enhanced disease pathogenesis and mortality.
Hence, determining the molecular mechanisms responsible for inflammatory cytokine production in the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection could provide future therapeutic targets.
Corresponding author Dr Elmostafa Bahraoui from the Université Paul Sabatier told Thailand
Medical News
span>, “The relative contribution of each pathway in immune protection or pathogenesis warrants further studies. It should be noted that past studies showed that unlike the E protein, the S protein does not seem to induce a significant inflammatory reaction. This difference underlines the importance of considering the E protein as a therapeutic target. Our study findings showed that E protein induced CXCL8 production in TLR2- and NF-κB dependent manner when tested in HEK-TLR2 cell line model. Thus, this model provides an important tool that could be used to screen antagonist compounds which can be used as antiviral drugs. The production of CXCL8, a 519 known neutrophil chemoattractant, is consistent with the reports describing a high circulating neutrophil number and associated injury in the airway and lung tissues in COVID-19 patients.”
The study is the first to use a detailed molecular characterization to demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 40 Envelope E protein binds to TLR2 receptor.
The study findings specifically showed that SARS-CoV-2 41 Envelope E protein binds to TLR2 in a direct, specific and dose-dependent manner.
Investigating signaling events that control downstream activation of cytokine production showed that E protein / TLR2 binding leads to the activation of NF-κB transcription factor that control the expression of multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines including CXCL8.
The study findings also lead to the possibility of using TLR4 antagonists such as Eritoran to reduce cytokine/chemokine production and alleviate disease symptoms.
The study findings suggest considering the envelope protein E as a novel target for COVID-19 46 interventions
For the latest
SARS-CoV-2 Research, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
