SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction And Exhibits Warburg Effect, Leading To Redox Shift And Cellular Anabolism
Thailand Medical - SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins - Mitochondrial Dysfunction - Wedox Shifarburg Effect - Redox Shift - Cellular Anabolism Jul 03, 2023 2 years, 7 months, 1 week, 3 days, 19 hours, 43 minutes ago
This unrelenting anabolism leads to the cytokine storm, chronic fatigue, chronic inflammation or neurodegenerative diseases. Drugs such as Lipoic acid and Methylene Blue have been shown to enhance the mitochondrial activity, relieve the Warburg effect and increase catabolism.
Thailand Medical: The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has brought unprecedented challenges to the world, and researchers have been working relentlessly to understand the intricate mechanisms behind the virus's effects on the human body. Recent studies have shed light on intriguing connections between the SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins and cellular processes, providing new insights into the development of long-term complications and potential treatment options.
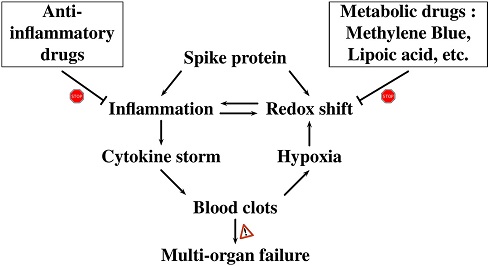 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Researchers from prestigious institutions worldwide, including Assistance Publique des Hôpitaux de Paris in France, Centro Médico Jurica in Mexico, Université de Strasbourg in France, Mediterranean Institute for Life Sciences in Croatia, Cité des Sciences et de l’Industrie in France, and October University for Modern Sciences and Arts in Egypt, have joined forces to explore the underlying mechanisms leading to redox shift, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cellular anabolism induced by the virus.
For those who are not aware, in oncology, the Warburg effect is the observation that most cancer cells produce energy predominantly not through the 'usual' citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria as observed in normal cells, but through a less efficient process of 'aerobic glycolysis' consisting of a high level of glucose uptake and glycolysis followed by lactic acid fermentation taking place in the cytosol, not the mitochondria, even in the presence of abundant oxygen.
The Study's Core Findings
The research proposes that COVID-19 infection triggers a significant anabolism process in the cells, which is driven by mitochondrial impairment and the Warburg effect. Anabolism, the buildup of complex molecules, results from an imbalance between the cell's energy-producing processes (catabolism) and energy-consuming processes (anabolism). This unrelenting anabolism leads to serious consequences like the cytokine storm, chronic fatigue, chronic inflammation, and even neurodegenerative diseases.
The Role of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins
The binding of the virus's spike proteins to the ACE2 receptor on the host cell surface is a redox phenomenon. This interaction is influenced by the presence of cysteine (Cys) residues, particularly Cys480-Cys488 in the spike protein and Cys133 and Cys141 in the ACE2 receptor. Disruptions in the redox balance of these residues significantly affect the binding affinity between the virus and the host cell.
The Virus's Predilection for a Reduced Environment
COVID-19 is more virulent in a reduced ce
llular environment, particularly in the elderly and individuals with metabolic syndrome or chronic diseases. Aging and chronic inflammatory conditions lead to a poor control of the redox balance in the body, contributing to a reduced extracellular environment and increased susceptibility to COVID-19 infection.
The Cytokine Storm Connection
The cytokine storm, a harmful overreaction of the immune system, is a redox phenomenon caused by increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). The dysregulation of redox signaling pathways can lead to excessive cytokine production and immune system activation, contributing to severe COVID-19 symptoms.
Long-Term Covid-19 Complications
COVID-19 can result in a variety of long-term complications, resembling a shift toward anabolic mode in cells, akin to premature aging. The study links the mitochondrial impairment seen in COVID-19 to other chronic diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's disease, all characterized by increased lactate concentrations and altered energy metabolism.
Corresponding author, Dr Laurent Schwart from the Assistance Publique des Hôpitaux de Paris told
Thailand Medical News, “A common consequence of COVID-19 appears to be chronic fatigue syndrome. It is a common disease characterized by decreased mitochondrial energy yield because of decreased oxidative phosphorylation. Multiple redox stress biomarkers, such as lower levels of antioxidants and higher levels of peroxides and superoxides, are linked to the severity of symptoms in chronic fatigue syndrome. These markers of redox iMeBalance also correlate with the severity of symptoms and elevated levels of ventricular lactic acid consistent with oxidative stress. Brain hypometabolism, akin to Alzheimer's disease, can be also seen. There is a concomitant increase in lactate acid levels in the blood characteristic of decreased oxidative phosphorylation.”
He added, “Many individuals who have been vaccinated with the mRNA vaccines triggering the synthesis of the viral spike protein in human cells can also suffer the same consequences as being infected!”
Promising Drug Interventions
The research highlights the potential of drugs such as Lipoic acid and Methylene Blue to enhance mitochondrial activity, relieve the Warburg effect, and promote catabolism. Combining Methylene Blue and Lipoic acid may offer therapeutic benefits in reducing long-term COVID-19 effects by stimulating catabolic processes.
Conclusion
This new research provides a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between the SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins, redox shift, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cellular anabolism. It unravels the connection between the Warburg effect and the cytokine storm, shedding light on the mechanisms underlying long-term complications of COVID-19. The findings open up new avenues for potential therapeutic interventions that target mitochondrial function and restore the balance between catabolic and anabolic processes in affected cells.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy redox balance and mitochondrial function to protect against the severe effects of COVID-19. It underscores the significance of preventive measures, such as lifestyle modifications and interventions targeting metabolic syndrome and chronic inflammatory conditions, to reduce the risk of infection and severe disease progression.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Free Radical Biology and Medicine.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0891584923005014
For the latest COVID-19 Research, keep on logging to
Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-study-proposes-redox-hypothesis-to-explain-as-to-why-certain-individuals-are-vulnerable-to-sars-cov-2-antioxidants-can-help-
