BREAKING COVID-19 NEWS: Study Finds That m6A Methylation Plays A Key Role COVID-19 Infections!
Thailand Medical News Team Aug 21, 2023 2 years, 5 months, 2 weeks, 4 days, 1 hour, 26 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The world has been grappling with the COVID-19 pandemic since its discovery in 2019. This disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus has shown a wide range of clinical manifestations, from mild infections to severe pneumonia. Factors like age, diabetes, and hypertension have been linked to higher risks of severe illness and death among COVID-19 patients. However, the reasons behind the differences in disease severity among various populations remain unclear.
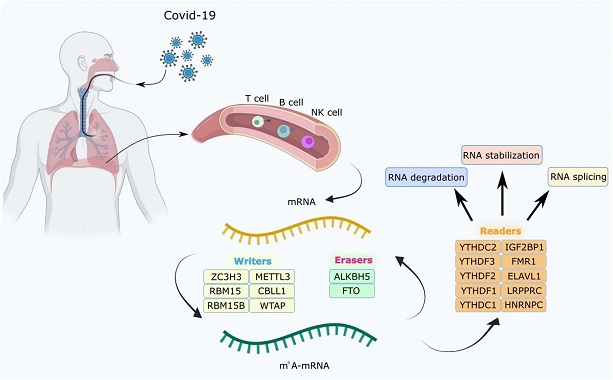 The overview of m6A RNA methylation modification in blood lymphocytes of patients infected with SARSCoV-2, including
The overview of m6A RNA methylation modification in blood lymphocytes of patients infected with SARSCoV-2, including
writers, readers, and erasers.
Researchers are keen to understand the underlying mechanisms and develop targeted treatments to combat COVID-19. Recent research from Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, has shed light on the significance of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation in COVID-19 infections.
Introduction to COVID-19 and m6A Methylation
COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has become a global health crisis, spreading rapidly through respiratory droplets and direct contact. While some drugs have been used to treat COVID-19, their effectiveness is still being studied.
Currently, supportive care remains the primary approach to managing the disease. Unraveling the molecular mechanisms behind COVID-19 and identifying potential therapeutic targets has become a pressing research topic.
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a common RNA modification found in various cellular RNAs. It involves the addition of methyl groups to adenine bases in RNA molecules and plays a vital role in processes like transcription, translation, and RNA splicing. Recent findings have connected m6A methylation to virus infections, including hepatitis viruses and HIV. Now, researchers have discovered that m6A methylation is closely associated with COVID-19 infections, providing a new avenue for investigation.
Understanding RNA m6A Methylation
RNA m6A methylation is a chemical modification occurring at the sixth position of adenine bases in RNA molecules. It is widespread in various types of RNA in cells and is crucial for regulating RNA-related processes. This modification mainly occurs in specific sequences and is dynamically reversible due to the action of enzymes that add (writers), remove (erasers), and recognize (readers) m6A marks. This process is essential for controlling gene expression, translation, and RNA stability.
Impact of m6A Methylation on COVID-19 Infection
Research has revealed that m6A modification has a significant impact on the transmission and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. Studies have shown that m6A modification levels change in host cells infected by the virus, affecting various aspects of viral replication and interaction with the host's immune system. Alterations in m6A-related genes have been observed in blood leukocytes and lung tissues of COVID-19 patients, suggesting a potential role in disease severity and immune response.
Severe COVID-19 cases are often characterized by an overactive immune response and excessive inflammation, including the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Studies and p
ast
COVID-19 News reports have indicated that m6A methylation can influence immune cell responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-infections-lead-to-cellular-m6a-rna-methylation-loss-in-host-cells-possible-implications-for-cancer-and-other-issues
Researchers have observed changes in m6A-related genes after infection, impacting immune pathways and inflammatory genes. This suggests that m6A methylation could be a key mechanism regulating immune responses during COVID-19 infections.
m6A Methylation and SARS-CoV-2 Evolution
The research has also highlighted the role of m6A methylation in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2. By analyzing the virus's genetic material, scientists have identified specific m6A modification sites that affect viral replication and adaptation. Mutant strains with altered m6A sites have emerged in different regions of the world, demonstrating the virus's ability to evolve to evade host immune responses. This discovery opens up new avenues for understanding how the virus evolves and develops resistance.
Utilizing m6A Methylation for Diagnosis and Treatment
The connection between m6A methylation and COVID-19 has paved the way for innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Researchers have developed prediction models based on m6A-related genes to assess the risk of COVID-19 infection accurately. By analyzing these genes, scientists can predict disease onset and progression in the early stages, aiding in timely intervention.
Moreover, m6A-related regulators are being explored as potential targets for vaccine development and antiviral drugs. By manipulating m6A modification-related genes, researchers can weaken the virus's virulence and design attenuated vaccine viruses. Small molecule drugs that target m6A-related pathways are also being investigated for their potential to treat COVID-19. These developments offer promising strategies to combat the disease effectively.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The recent study on m6A methylation's role in COVID-19 infections has opened up new horizons for understanding the disease and developing effective treatments. As our understanding of m6A methylation deepens, more targeted therapies and diagnostic tools are likely to emerge. By targeting m6A-related pathways, scientists can potentially control immune responses, reduce inflammation, and develop antiviral drugs that specifically target the virus's vulnerabilities. As the global fight against COVID-19 continues, the insights gained from m6A methylation research could prove instrumental in overcoming this pandemic and preventing future outbreaks.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Cell Death Discovery.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41420-023-01580-1
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
