BREAKING NEWS! Researchers Find That SARS-CoV-2 Contributes to Oral Cancer Progression, Treatment Resistance And Tumor Recurrence!
Thailand Medical - SARS-CoV-2 - Oral Cancer Progression -Treatment Resistance - Tumor Recurrence Jul 10, 2023 2 years, 7 months, 2 weeks, 11 hours, 52 minutes ago
Scientists Identify Cellular Mechanisms Amplifying the Impact of COVID-19 On Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC)
Thailand Medical: In a new study conducted by a team of researchers from various Iranian universities, i.e. the Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Islamic Azad University, Universal Scientific Education & Research Network (USERN), Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Kerman University of Medical Science, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, and Tarbiat Modares University, an intriguing connection has been discovered between COVID-19 and the progression, chemo-resistance, and tumor recurrence of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
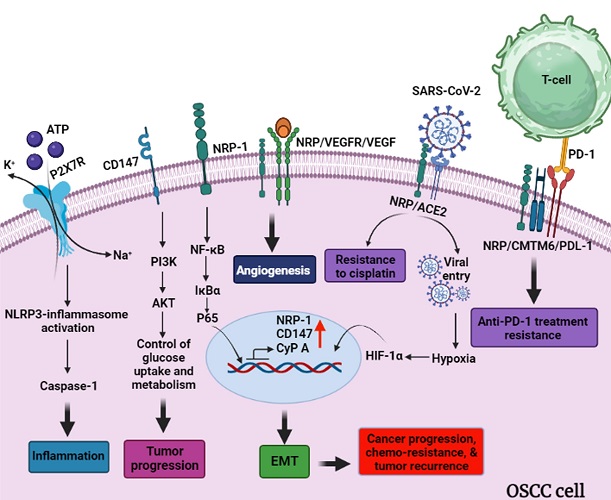 The illustration indicates cellular events of oral-squamous cell carcinoma and its communication with COVID-19 infection: evaluation of neuropilin (NRP) on tumor cells and its interaction with CMTM6 and PDL-1 leads to “resistance to anti-PD-1 treatment”. Interaction of NRP with ACE2 causes resistance to cisplatin and facilitation of viral entry (hypoxia caused by covid-19 infection leads to NRP-1 expression). NRP facilitates angiogenesis activity of the VRGF/VEGFR axis. On the other hand, NRP-1 singly evaluates EMT in tumor cells through NF-κB/IκBα/P65. Regulation of glucose uptake and metabolism is a crucial factor in tumor progression. CD147 on the tumor cell membrane helps tumor cells to control this event through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. P2X7R is one of the receptors that are elevated on the tumor membrane; the activity of P2X7R leads to NLRP3-inflammasome and caspase-1 activation which results in inflammation
The illustration indicates cellular events of oral-squamous cell carcinoma and its communication with COVID-19 infection: evaluation of neuropilin (NRP) on tumor cells and its interaction with CMTM6 and PDL-1 leads to “resistance to anti-PD-1 treatment”. Interaction of NRP with ACE2 causes resistance to cisplatin and facilitation of viral entry (hypoxia caused by covid-19 infection leads to NRP-1 expression). NRP facilitates angiogenesis activity of the VRGF/VEGFR axis. On the other hand, NRP-1 singly evaluates EMT in tumor cells through NF-κB/IκBα/P65. Regulation of glucose uptake and metabolism is a crucial factor in tumor progression. CD147 on the tumor cell membrane helps tumor cells to control this event through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. P2X7R is one of the receptors that are elevated on the tumor membrane; the activity of P2X7R leads to NLRP3-inflammasome and caspase-1 activation which results in inflammation
This unprecedented revelation sheds light on the potential risks faced by OSCC patients during the pandemic, urging the need for targeted therapies to combat these challenges. The study's findings have sparked a global conversation among scientists, medical professionals, and the public alike.
Already
Thailand Medical News has been warning for a while that SARS-CoV-2 is an oncogenic virus that can trigger the onset of various cancers and the fact that it also affects many cellular pathways that are involved in upregulating oncogenic genes and also suppressing tumor protective genes while creating persistent inflammation.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/2021-peer-reviewed-study-warning-that-covid-19-can-lead-to-pancreatic-adenocarcinoma-seems-to-be-holding-true-as-pancreatic-cancer-cases-rise
(READ ALL THE LINKS AT THE END OF THE ARTICLE)
A Deadly Convergence
The research, based on comprehensive studies and analysis, establishes a compelling case for heightened vulnerability among OSCC patients to severe COVID-19 symptoms, as well as increased cancer progression and treatment failure. With OSCC being the fifth most common cancer worldwide, affecting over 300,000 individua
ls annually, the ramifications of this newfound link are far-reaching.
Understanding the Mechanisms
To comprehend how the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) contributes to OSCC complications, the study elucidates the cellular and molecular mechanisms at play. The researchers identified specific receptors and signaling pathways triggered by the virus that may fuel OSCC progression, including the Eph receptor, neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), P2X7 receptor, and CD147.
By binding to these receptors, the virus may activate various downstream signaling pathways implicated in cancer progression. For example, the study suggests that the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 can bind to ephrin receptors, NRP-1, and P2X7 receptors found on OSCC cells, triggering signaling pathways such as NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB, JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, mTOR, and HIF-1α.
Eph Receptor: Infections caused by SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses have been shown to exploit Eph receptors and ephrin ligands, proteins involved in cell signaling, to invade host cells and modulate crucial pathways. The study reveals a possible association between Eph receptors and the development of OSCC in patients.
NRP-1: The study also highlights the role of neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) as a potential therapeutic target in OSCC. NRP-1, which is significantly overexpressed in OSCC patients, has been linked to enhanced tumor growth, angiogenesis, and chemo-resistance. By unraveling the connection between NRP-1 and SARS-CoV-2, the study team hoped to pave the way for innovative interventions that can curtail OSCC progression.
P2X7 Receptor: The hyperactivation of the P2X7 receptor, induced by increased extracellular ATP levels resulting from SARS-CoV-2 infection, may further exacerbate OSCC progression. Understanding the role of this receptor in tumor growth and metastasis holds great promise for future therapeutic strategies.
CD147: CD147, also known as EMMPRIN, emerges as a key player in OSCC development. Its overexpression has been associated with tumor growth, metastasis, drug resistance, and the facilitation of SARS-CoV-2 invasion.
Implications and Future Directions
The alarming study findings underscores the urgent need for therapeutic interventions that mitigate the risks faced by OSCC patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. By targeting specific receptors and downstream signaling pathways, novel pharmacological therapies can potentially disrupt OSCC progression, reduce chemo-resistance, and prevent tumor recurrence. The findings offer hope to millions of OSCC patients worldwide, providing a new path forward in the fight against cancer.
Looking ahead, the researchers emphasize the importance of continued investigations to unveil additional mechanisms through which SARS-CoV-2 may impact OSCC progression. By expanding our understanding of these mechanisms, researchers can develop even more effective therapeutic strategies tailored to OSCC patients, offering them improved outcomes and a brighter future.
Conclusion
The groundbreaking research conducted by Iranian scientists has revealed a fascinating and significant link between COVID-19 and the progression, chemo-resistance, and tumor recurrence of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). By elucidating the cellular and molecular mechanisms triggered by SARS-CoV-2, this study has opened up new avenues for targeted therapies and interventions
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Oral Oncology (Science Direct)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1368837523001793
For the latest SAR-CoV-2 Research, keep on logging to
Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/diy-guide-for-checking-for-mouth-or-oral-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/cancer-news-john-hopkins-study-shows-that-the-more-oral-sex-one-indulges-in,-the-higher-the-risks-of-developing-oropharyngeal-cancer
