COVID-19 News: Study Review Shows That Curcumin Is A Potential Antiviral Agent And Immune-Inflammatory Modulator In COVID-19
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 04, 2023 2 years, 3 months, 3 weeks, 2 hours, 45 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The ongoing global COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has left an indelible mark on the world. With over 700 million confirmed cases and 7 million deaths, the search for effective treatments and preventive measures remains a top priority. The disease's pathophysiology involves a complex interplay of factors, including an exaggerated immune and inflammatory response, coagulopathy, endothelial damage, and the dreaded cytokine storm. While vaccines and antiviral drugs have been at the forefront of treatment efforts, researchers have been exploring alternative approaches, including the use of natural compounds such as curcumin, the primary bioactive constituent of Curcuma longa, for potential therapeutic benefits.
.jpg)
Curcumin, an ancient remedy that has been widely used in traditional medicine, has been the subject of numerous pharmacological investigations and clinical trials due to its broad spectrum of pharmacological activities. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and considered safe for consumption, curcumin's antiviral properties have gained significant attention in recent years. It has shown effectiveness against various RNA and DNA viruses, including HIV, Influenza A, HSV-2, and Cytomegalovirus, as well as coronaviruses. These properties have sparked interest in curcumin as a potential treatment for COVID-19.
Scientometric Analysis: Mapping Curcumin's Role in COVID-19 Research
Scientometric analysis is a powerful tool for understanding the landscape of scientific research by systematically evaluating the published literature and identifying trends and key focus areas. However, despite the growing body of research on curcumin and its potential in COVID-19 treatment, a comprehensive scientometric analysis of this topic had not been conducted until now. To bridge this gap, a team of researchers from the Department of Respiratory Medicine at the Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China embarked on a journey to provide a holistic view of curcumin's role in the context of COVID-19.
Methods
The study encompassed a systematic search of the Web of Science core collection database, covering literature published from January 1, 2020, to December 31, 2022. Keywords such as 'curcumin,' 'COVID-19,' and their synonyms were employed to retrieve relevant publications. The analysis utilized various scientific tools, including VOSviewer, Origin 2023, and Charticulator, combined with external data sources.
Results
The comprehensive analysis yielded a total of 252 publications for review, representing a broad international effort. These publications originated from 63 different countries and territories, with India leading the way in terms of the number of contributions. The research was disseminated across 170 different journals, emphasizing the global interest in the subject matter. Notably, the Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB) emerged as a key institution driving this research.
The most influential publication in this domain had been cited a remarkable 166 times, indicating the growing interest in curcumin's potential in COVID-19 treatment. The analysis unveiled key themes in the research, with a strong focus on curc
umin's antiviral properties and its role in modulating the immune-inflammatory response, particularly in mitigating the cytokine storm associated with severe COVID-19 cases. Furthermore, the pharmacological mechanisms of curcumin in COVID-19 treatment have gained substantial attention, and there is a growing body of evidence supporting the clinical use of curcumin to enhance outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
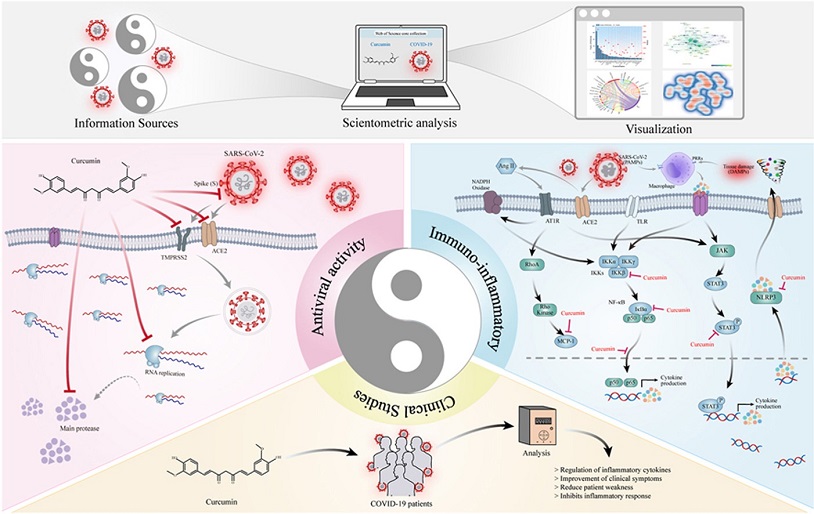
Antiviral Activity of Curcumin
One of the primary areas of interest in curcumin's role in COVID-19 is its antiviral activity. Curcumin has demonstrated a broad spectrum of antiviral effects, making it a potential candidate for combating various viruses, including coronaviruses. Its antiviral mechanism extends throughout the entire viral life cycle, including virus attachment, entry, protein replication, and direct virus inactivation. This has been covered in numerous studies and also past
COVID-19 News reports.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/observational-clinical-study-shows-that-curcumin-with-catechin-improves-covid-19-infected-patient-s-inflammatory-conditions
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/observational-clinical-study-shows-that-curcumin-with-catechin-improves-covid-19-infected-patient-s-inflammatory-conditions
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-german-study-shows-that-phytochemicals-from-turmeric-inhibit-sars-cov-2-in-vitro-and-could-be-used-as-potential-therapeutics-for-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-german-study-shows-that-phytochemicals-from-turmeric-inhibit-sars-cov-2-in-vitro-and-could-be-used-as-potential-therapeutics-for-covid-19
Importantly, curcumin has shown significant effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19.
Studies have revealed that curcumin can inhibit the binding of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to the ACE2 receptor, which serves as the gateway for the virus to enter host cells. This interaction has been validated in in vitro studies, underscoring curcumin's potential in preventing viral entry. Furthermore, in silico studies have demonstrated curcumin's ability to bind to the major protease of SARS-CoV-2, inhibiting its activity.
In addition to blocking viral entry, curcumin has been shown to hinder viral replication at multiple levels. This includes inhibiting the replication of negative-strand RNA and interfering with the virus's structural integrity. All these mechanisms highlight curcumin's multifaceted role in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 replication.
Immune-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Curcumin
The immune and inflammatory response in COVID-19 is a critical factor in disease progression, with the infamous cytokine storm playing a pivotal role. Severe COVID-19 cases are associated with elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, contributing to poor prognosis and complicated clinical outcomes. Curcumin has shown remarkable anti-inflammatory properties, offering a potential solution to mitigate cytokine storms.
Curcumin effectively reduces the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF, in COVID-19 patients. These cytokines are major contributors to the cytokine storm, and curcumin's ability to suppress them is a key focus of research. In addition to these findings, curcumin can influence several pathways involved in the immune-inflammatory response. It can regulate the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) by reducing MCP-1 expression, preventing the overstimulation of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R), and thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Curcumin also targets pathways like JAK/STAT and NF-κB, which are central to the cytokine storm, further contributing to its anti-inflammatory effects.
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Furthermore, curcumin is capable of enhancing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, which can counterbalance the pro-inflammatory response. This bidirectional regulatory effect of curcumin on cytokines is particularly important in managing the cytokine storm, making it an attractive candidate for COVID-19 treatment.
Clinical Application of Curcumin in COVID-19
Intriguingly, the scientometric analysis identified registered clinical trials that utilized curcumin to treat COVID-19 patients. These trials explored various forms of curcumin, such as nanocurcumin, nanomicelles, and combinations with other natural products and vitamins. The results of these trials have provided compelling evidence for curcumin's clinical efficacy in improving COVID-19 outcomes.
Nanocurcumin, in particular, has demonstrated its potential in modulating the inflammatory response and improving clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients. The use of nanocurcumin resulted in reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhanced recovery. In addition, nanomicelles containing curcumin have shown promise in expediting recovery from acute inflammation during the inflammatory phase of COVID-19. Combinations of curcumin with other natural products and vitamins, such as curcumin, vitamin C, and glycyrrhizic acid, have also proven effective in regulating immune and inflammatory responses associated with coronavirus infections. Clinical trials combining curcumin with quercetin and vitamin D3 have expedited viral clearance, improved symptoms, and reduced excessive inflammatory responses, further highlighting the potential of curcumin in the clinical setting.
Future Trends
As the scientometric analysis provided a snapshot of the current state of curcumin research in the context of COVID-19, it also pointed to potential future research trends and areas of exploration. One key direction is drug design, where curcumin holds immense promise. Despite being widely available as a food ingredient, curcumin's bioavailability can be improved through innovative drug formulations. Nanocurcumin, in particular, has demonstrated superior bioavailability and efficacy, offering a path for future drug development.
However, it is essential to conduct more extensive, multi-center, and large-sample clinical trials to validate these findings and optimize dosages.
Another intriguing avenue of research is the combination of curcumin with natural products or vitamins. Studies have shown that such combinations can regulate immune and inflammatory responses, presenting a potentially potent strategy against coronavirus infections. The future might see more investigations into these combinations and their therapeutic potential in the management of COVID-19.
Additionally, curcumin's application as a photosensitizer for combating SARS-CoV-2 in vitro has raised intriguing possibilities. Future research may delve deeper into this area to explore the potential of curcumin-based photodynamic therapy as an alternative approach to fighting the virus.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the study findings provide valuable insights into the evolving landscape of curcumin research in the context of COVID-19. The study highlights the pivotal role of curcumin in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 replication, modulating immune-inflammatory responses, and improving clinical outcomes. This emerging research field not only focuses on the fundamental mechanisms of curcumin but also demonstrates its potential clinical applications.
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to be a global concern, the potential of curcumin in prevention and treatment remains an area of substantial and sustained advancement. The scientometric analysis not only serves as a foundation for researchers but also underscores the importance of ongoing investigations into the multifaceted properties of curcumin in the fight against COVID-19. With promising clinical trials and innovative drug formulations on the horizon, curcumin's role in COVID-19 treatment is poised for further development and exploration, offering a ray of hope in these challenging times.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Heliyon.
https://www.cell.com/heliyon/fulltext/S2405-8440(23)08856-4
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/80-percent-of-curcumin-supplies-and-supplements-contaminated-by-lead
.jpg)
