COVID-19 Causes Morphological Changes Of Red Blood Cells, Leading To Microangiopathy, Microthrombosis, Impaired Blood Flow/Tissue Oxygenation
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Apr 02, 2024 1 year, 10 months, 3 weeks, 3 days, 10 hours, 32 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The COVID-19 pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has brought about unprecedented challenges to global health. While initially characterized primarily as a respiratory illness, it has become increasingly evident that COVID-19 can affect multiple organ systems, leading to a range of complications that extend beyond the lungs. Among the critical aspects of COVID-19 pathophysiology is its influence on red blood cells (RBCs) and microcirculation, which play pivotal roles in oxygen transport and tissue perfusion. This
COVID-19 News report is based on a study by researchers from Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus-Senftenberg-Germany and University of Lyon I- France that aims to delve into the intricate relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the morphological changes observed in RBCs, discussing their implications for microangiopathy, microthrombosis, and impaired tissue oxygenation.
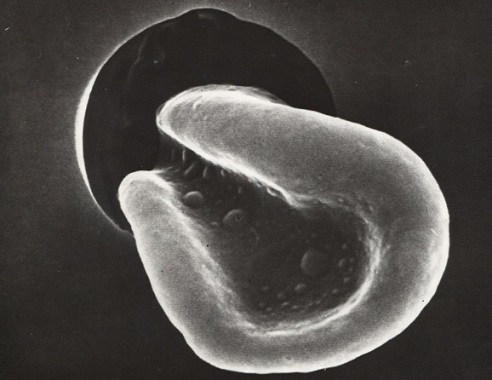 COVID-19 Causes Morphological Changes Of Red Blood Cells,
COVID-19 Causes Morphological Changes Of Red Blood Cells,
Leading To Microangiopathy, Microthrombosis, Impaired Blood
Flow/Tissue Oxygenation
Thailand
Medical News had previously also covered studies showing that SARS-CoV-2 causes morphological changes to the red blood cells and also impairs its oxygen transportation capabilities.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-affects-red-blood-cell-morphology
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-affects-red-blood-cell-morphology
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-causes-deformation-of-red-blood-cells,-leading-to-anemia
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-impairs-oxygen-delivery-by-altering-red-blood-cell-hematological,-hemorheological-and-oxygen-transport-properties
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-german-and-swiss-researchers-discover-increased-red-blood-cell-deformation-in-children-and-adolescents-after-sars-cov-2-infection
rch-reveals-that-covid-19-attacks-hemoglobin-in-red-blood-cells,-rendering-it-incapable-of-transporting-oxygen--current-medical-protoco">https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/must-read-research-reveals-that-covid-19-attacks-hemoglobin-in-red-blood-cells,-rendering-it-incapable-of-transporting-oxygen--current-medical-protoco
Interaction Between SARS-CoV-2 and Red Blood Cells
While angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors, the primary cellular entry points for SARS-CoV-2, are not expressed on RBCs, emerging evidence suggests that the virus can interact with these cells through alternative receptors or auxiliary membrane proteins. This interaction leads to notable damage to RBCs, altering their morphology, deformability, and aggregability. Studies have indicated that COVID-19 infection is associated with significant changes in RBC characteristics, such as increased rigidity and enhanced aggregation tendencies, which can impact their functional role in oxygen transport and microcirculation.
Mechanisms of Red Blood Cell Dysfunction
The dysfunction of RBCs in COVID-19 patients can be attributed to several mechanisms. Immunological processes, including cytokine storms triggered by viral infection, contribute to RBC alterations. These processes can lead to oxidative stress, membrane damage, and changes in RBC membrane proteins, affecting their deformability and aggregability. Additionally, COVID-19-associated microangiopathy, characterized by endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation, further exacerbates RBC dysfunction. These multifaceted mechanisms collectively contribute to impaired RBC function observed in COVID-19 patients.
Impact on Microcirculation
The morphological changes in RBCs due to COVID-19 have significant implications for microcirculatory function. Enhanced RBC deformability hinders their passage through capillaries, affecting oxygen delivery to tissues. Moreover, increased RBC aggregation contributes to microvascular thrombotic events, further compromising tissue perfusion. These microcirculatory disturbances are central to the pathogenesis of COVID-19-related complications, including organ dysfunction and hypoxia. Studies have shown that COVID-19 patients often exhibit microvascular abnormalities, such as capillary congestion and thrombosis, underscoring the impact of RBC dysfunction on microcirculation.
Role of Endothelial Cells in Microvascular Dysfunction
Endothelial cells play a pivotal role in maintaining vascular homeostasis and regulating blood flow. In COVID-19, endothelial dysfunction is a key driver of microvascular complications. SARS-CoV-2 infection of endothelial cells leads to endotheliitis, disrupting vascular integrity and promoting a prothrombotic state. Endothelial dysfunction also contributes to increased vascular permeability, allowing inflammatory cells and factors to enter tissues, further exacerbating tissue injury. These endothelial disturbances, coupled with RBC dysfunction, exacerbate microcirculatory dysfunction and tissue hypoxia, contributing to the severity of COVID-19 pathology.
Clinical Implications and Therapeutic Considerations
Understanding the complex interplay between SARS-CoV-2, RBCs, and endothelial cells has critical clinical implications. Monitoring RBC morphology and function in COVID-19 patients may provide insights into disease severity and prognosis. Therapeutic strategies targeting RBC deformability, endothelial function, and microcirculatory integrity hold promise in mitigating COVID-19-related microvascular complications. Anticoagulant therapy, anti-inflammatory agents, and interventions aimed at preserving endothelial function are areas of active research and clinical investigation in the management of COVID-19 patients with microvascular involvement.
Conclusion
COVID-19's impact extends beyond respiratory manifestations to affect multiple organ systems, including the microcirculation. The interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and red blood cells leads to morphological changes that impair RBC function and contribute to microangiopathy, microthrombosis, and tissue hypoxia. Endothelial dysfunction further exacerbates these microvascular disturbances, highlighting the need for targeted therapeutic interventions to address COVID-19-related microcirculatory complications effectively. Continued research efforts aimed at elucidating the mechanisms underlying these interactions and developing innovative therapeutic strategies are essential in improving outcomes for COVID-19 patients with microvascular involvement.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Life
https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/14/4/460
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-study-shows-that-asymptomatic-covid-19-infections-end-up-with-sub-clinical-vascular-damage-and-red-blood-cell-turnover
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-belgium-study-finds-that-covid-19-can-cause-erythropoiesis-alterations,-inflammatory-anemia-and-prevalence-of-positive-coombs-tests
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-that-sars-cov-2-infections-can-either-cause-onset-of-anemia-or-exacerbate-the-effects-of-anemia-for-those-already-with-the-condition
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-doctors-warns-that-sars-cov-2-infections-can-cause-pancytopenia-increasing-incidences-sparks-concerns
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-also-infects-and-impairs-hematopoietic-stem-cells
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-shows-that-red-blood-cells-play-a-role-in-multi-organ-spread-of-sars-cov-2
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-news-study-shows-that-release-of-immature-blood-cells-from-bone-marrow-signifies-covid-19-severity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-latest-sars-cov-2-may-target-red-marrow-and-prevent-formation-of-new-erythrocytes--vitamin-b12-supplementation-important
