Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News May 31, 2024 1 year, 8 months, 2 weeks, 2 days, 6 hours, 46 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on global health, with severe cases causing significant morbidity and mortality. Despite advancements in treatment and vaccination, the virus continues to mutate, posing ongoing risks of severe infection. One critical aspect of severe COVID-19 is the impairment of mitochondrial function in monocytes, leading to metabolic and immune dysregulation. This
COVID-19 News report explores the identification of mitochondrial dysfunction biomarkers in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection and highlights the potential of curcumin as a preventive phytomedicine.
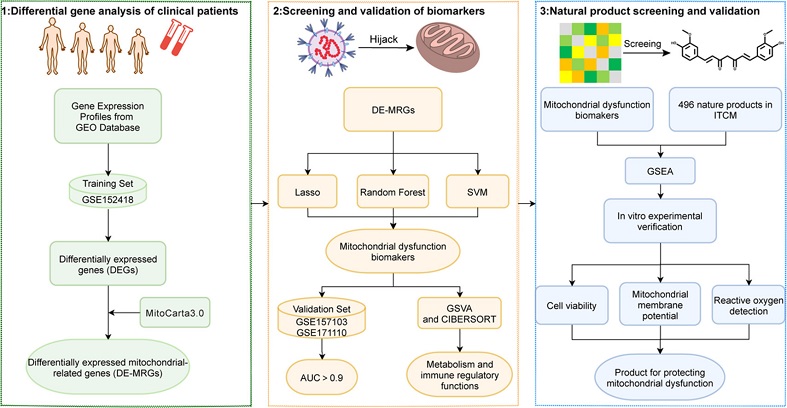 Graphical Abstract - Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers and Curcumin: New Hope for Severe COVID-19
The Role of Mitochondria in COVID-19 Severity
Graphical Abstract - Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers and Curcumin: New Hope for Severe COVID-19
The Role of Mitochondria in COVID-19 Severity
Mitochondria are essential organelles responsible for cellular energy metabolism and immune responses. During SARS-CoV-2 infection, the virus can hijack the host cell's mitochondria, causing metabolic dysfunctions that exacerbate the severity of the disease. Clinical evidence suggests that individuals with pre-existing mitochondrial metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes, are at a higher risk of developing severe COVID-19.
Metabolic and Immune Dysregulation
In severe COVID-19 cases, monocytes show signs of mitochondrial dysfunction, including reduced respiratory capacity and increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This mitochondrial impairment leads to an upregulation of glycolysis, promoting viral replication and inflammatory responses. Understanding the biomarkers associated with this dysfunction is crucial for developing targeted interventions.
Identifying Biomarkers of Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Researchers from Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Beijing Institute of Pharmacology & Toxicology conducted a comprehensive study to identify biomarkers of mitochondrial dysfunction in severe COVID-19 patients. The study involved differential gene analysis and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) on monocyte datasets to pinpoint genes and pathways distinguishing severe patients from uninfected individuals.
Key findings include:
-
Differential Gene Analysis: Identification of 1812 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between severe COVID-19 patients and healthy individuals, with 1390 upregulated and 422 downregulated genes.
-Mitochondrial-Related Pathways: Enrichment analysis revealed significant dysregulation in 17 mitochondrial processes, highlighting the central role of mitochondrial dysfunction in severe cases.
Biomarker Identification
By intersecting the DEGs with the MitoCarta 3.0 gene set, researchers identified 77 differentially expressed mitochondrial-related genes (DE-MRGs). Machine learning algorithms further refined this list to five key biomarkers: RECQL4, PYCR1, PIF1, POLQ, and GLDC. These biomarkers showed high predictive accurac
y in distinguishing severe COVID-19 cases from mild or uninfected individuals, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) greater than 0.9.
Exploring the Impact of Biomarkers on Metabolism and Immunity
The identified biomarkers were analyzed using GSVA and CIBERSORT algorithms to explore their effects on metabolic pathways and immune cell populations. The results demonstrated significant correlations between these biomarkers and dysregulated metabolic processes, as well as immune cell imbalances in severe COVID-19 patients.
Curcumin: A Promising Phytomedicine - Predictive Model and Experimental Validation
To identify potential natural compounds that could mitigate severe COVID-19, researchers screened 496 natural compounds using a predictive model based on the dysregulated mitochondrial-related genes. Curcumin emerged as the top candidate, with significant potential to prevent the progression to severe infection.
In Vitro Experiments
Pre-treatment with curcumin for eight hours showed promising results in alleviating mitochondrial membrane potential damage and reducing ROS levels caused by the SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein. These findings suggest that curcumin could play a crucial role in protecting mitochondrial function and preventing severe COVID-19.
Conclusion
The study provides compelling evidence that mitochondrial dysfunction is a key factor in the severity of COVID-19. The identified biomarkers, RECQL4, PYCR1, PIF1, POLQ, and GLDC, are crucial for understanding the metabolic and immune changes in severe cases. Furthermore, curcumin presents a promising natural compound for mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction and preventing severe disease progression. These findings pave the way for new strategies in predicting and intervening early in SARS-CoV-2 infections, potentially improving patient outcomes and alleviating the burden on healthcare systems.
Future Directions
Further research is needed to validate these findings in larger clinical trials and explore the therapeutic potential of curcumin and other natural compounds in treating severe COVID-19. Understanding the intricate relationship between mitochondrial function and immune responses will be crucial in developing effective interventions for current and future viral infections.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Phytomedicine.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0944711324004422
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-review-shows-that-curcumin-is-a-potential-antiviral-agent-and-immune-inflammatory-modulator-in-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/observational-clinical-study-shows-that-curcumin-with-catechin-improves-covid-19-infected-patient-s-inflammatory-conditions
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-herbs-randomized-controlled-trial-shows-that-curcumin-offers-anti-inflammatory-benefits-for-adults-recovering-from-covid-19-and-are-vaccinate
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-german-study-shows-that-phytochemicals-from-turmeric-inhibit-sars-cov-2-in-vitro-and-could-be-used-as-potential-therapeutics-for-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/must-read-covid-19-supplements-chinese-researchers-in-wuhan-discover-that-curcumin-has-antiviral-effects-on-certain-coronaviruses
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-shows-curcumin,-cinnamon-and-resveratrol-health-supplements-effective-in-prevention-and-management-of-diabetes
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-non-drug-curcumin-based-nanocapsules-as-antibiotics-to-fight-superbugs-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/pentagamavumon-1-(pgv-1)-extracted-from-turmeric-(curcumin)-shows-promise-in-treating-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/80-percent-of-curcumin-supplies-and-supplements-contaminated-by-lead
