Herbs And Phytochemicals: Merits Of Angelica Sinensis Against Cardiovascular And Cerebrovascular Diseases
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 02, 2024 1 year, 9 months, 2 weeks, 4 hours, 11 minutes ago
Herbs And Phytochemicals: In the realm of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, commonly known as Dong Quai or Danggui, has garnered considerable attention for its therapeutic potential in addressing various health ailments, particularly cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Recent studies and research have shed light on the intricate pharmacological mechanisms and active compounds within Angelica sinensis, paving the way for a deeper understanding of its efficacy in promoting vascular health and mitigating the risk factors associated with heart and brain-related disorders.
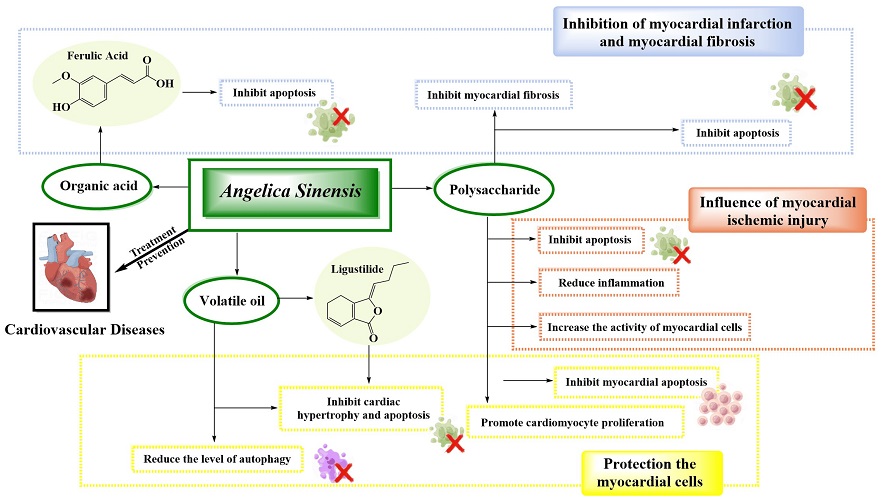 Mechanisms of Angelica-Sinensis and its compounds in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Mechanisms of Angelica-Sinensis and its compounds in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
This
Herbs And Phytochemicals updated review study conducted by researchers from Liaoning University of International Business and Economics-China, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing-China and Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences)-China explores the merits of Angelica Sinensis in treatments involving cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Historical Significance and Traditional Usage
The roots of Angelica sinensis have been integral to Chinese medicine for centuries, revered for their ability to invigorate blood circulation, regulate menstruation, relieve pain, and nourish the intestines. Beyond its medicinal applications, Angelica sinensis has also been a staple in the traditional Chinese diet, valued for its rich nutrient profile comprising organic acids, volatile oils, phenolic acids, flavonoids, coumarin, polysaccharides, and amino acids. This dual role as both a therapeutic herb and a culinary ingredient underscores its holistic significance in promoting overall well-being.
Unraveling the Pharmacological Effects on Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) stand as a leading cause of mortality globally, characterized by conditions such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and myocardial infarction. Angelica sinensis has emerged as a promising agent in combating these ailments, thanks to its diverse array of bioactive compounds. Key among these are ferulic acid, ligustilide, senkyunolide H, and Z-butylidenephthalide, each contributing distinct pharmacological effects that synergistically enhance cardiovascular resilience.
-Myocardial Ischemic Injury: Protective Mechanisms
Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) poses a significant threat to cardiac health, marked by oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptotic cell death. Studies have demonstrated that polysaccharides derived from Angelica sinensis exhibit cardioprotective properties by modulating the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing inflammation, and inhibiting apoptosis. Similarly, volatile oils containing ligustilide showcase anti-inflammatory effects, further bolstering myocardial resilience against ischemic d
amage.
-Protection of Myocardial Cells: Mitigating Damage
Maintaining the integrity and function of myocardial cells is crucial in averting cardiovascular complications. Angelica sinensis, particularly its polysaccharides, exerts a protective influence by regulating gene expression, enhancing antioxidant defenses, and inhibiting apoptotic pathways. This cellular fortification translates into improved cardiac performance and resilience to pathological stressors.
-Inhibition of Myocardial Infarction and Fibrosis: Combatting Structural Damage
Myocardial infarction (MI) and subsequent fibrotic changes are hallmarks of advanced cardiovascular pathology. Angelica sinensis intervenes by attenuating inflammatory responses, inhibiting fibrosis-promoting factors, and enhancing mitochondrial function. These actions collectively mitigate structural damage, preserve cardiac function, and impede the progression of heart-related complications.
Exploring Angelica Sinensis in Cerebrovascular Health
Cerebrovascular diseases, encompassing conditions like ischemic stroke and vascular dementia, pose grave neurological challenges. Angelica sinensis emerges as a therapeutic ally in safeguarding brain health through multifaceted mechanisms.
-Mitigating Cerebral Ischemic Injury: Neuroprotective Strategies
Ischemic cerebral vascular disease (ICVD) exacts a toll on neuronal integrity, leading to cognitive impairment and neuronal loss. Angelica sinensis intervenes by reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammatory mediators, and promoting neuronal survival pathways. These actions converge to mitigate cerebral ischemic injury and preserve neurological function.
-Enhancing Vascular Dementia Resilience: Cognitive Support
Vascular dementia (VD) represents a cognitive decline stemming from cerebrovascular dysfunction. Angelica sinensis, especially its volatile oils and active constituents, enhances cognitive function, promotes neuronal plasticity, and combats neurodegenerative processes. These attributes position it as a potential therapeutic adjunct in managing cognitive disorders.
-Preservation of Brain Cells: Neuroprotection
The polysaccharides and volatile oils within Angelica sinensis exert neuroprotective effects by modulating cellular stress responses, inhibiting apoptotic pathways, and enhancing neuronal viability. These mechanisms safeguard brain cells from degeneration, offering promise in addressing conditions like Alzheimer's disease and ischemic vertigo.
Holistic Benefits Beyond Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Health
The therapeutic spectrum of Angelica sinensis extends beyond vascular health, encompassing diverse physiological systems and pathologies.
-Regulation of Blood Pressure and Lipids: Metabolic Harmony
Angelica sinensis components exhibit hepatoprotective effects, regulate lipid metabolism, and modulate vascular endothelial function. These attributes contribute to blood pressure regulation, lipid profile improvement, and atherosclerosis prevention, underpinning its holistic cardiovascular benefits.
-Anti-Atherosclerosis Mechanisms: Vascular Resilience
Atherosclerosis, a precursor to many cardiovascular complications, is mitigated by Angelica sinensis through anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating pathways. Its active compounds target key molecular cascades involved in plaque formation and vascular dysfunction, attenuating the progression of atherosclerotic disease.
-Protection of Vascular Endothelial Cells: Endothelial Resilience
Vascular endothelial cells play a pivotal role in vascular health, and Angelica sinensis aids in preserving their integrity and function. By enhancing nitric oxide production, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting endothelial growth factors, Angelica sinensis fortifies vascular endothelial resilience against pathological insults.
Harnessing the Potential: Future Directions
The evolving landscape of biomedical research continues to unveil the therapeutic potential of Angelica sinensis in combating cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and metabolic disorders. Future endeavors should focus on elucidating specific molecular targets, optimizing dosage regimens, and exploring synergistic formulations to maximize its clinical efficacy. Integration of Angelica sinensis into personalized medicine paradigms and preventive healthcare strategies holds promise in fostering vascular health and overall well-being across diverse populations.
In Conclusion
Angelica sinensis stands as a botanical beacon in traditional medicine, offering a treasure trove of bioactive compounds with profound therapeutic implications. From safeguarding cardiovascular resilience to fortifying neurological function, its versatile pharmacological repertoire underscores its relevance in modern healthcare. As research advances and clinical applications expand, Angelica sinensis is poised to emerge as a cornerstone in holistic health promotion, bridging ancient wisdom with contemporary medical paradigms.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Molecules.
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/29/9/2100
For the latest on
Herbs and Phytochemicals, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
