Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 07, 2024 1 year, 7 months, 3 weeks, 5 days, 10 hours, 44 minutes ago
Medical News: Gastric cancer (GC) ranks as the third leading cause of cancer deaths globally, with approximately one million new cases and 784,000 deaths annually. The disease's prevalence is particularly concerning as the world's population ages. Despite understanding various risk factors, such as Helicobacter pylori infection, salted food intake, and alcohol consumption, the etiology of gastric cancer remains incomplete. A recent study by researchers from Zhejiang University School of Medicine-China, Qingtian People’s Hospital-China and The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine-China that is covered in this
Medical News report, sheds light on an unexpected protective factor: hypothyroidism.
 Hypothyroidism Confers Protection Against Risk of Gastric Cancer
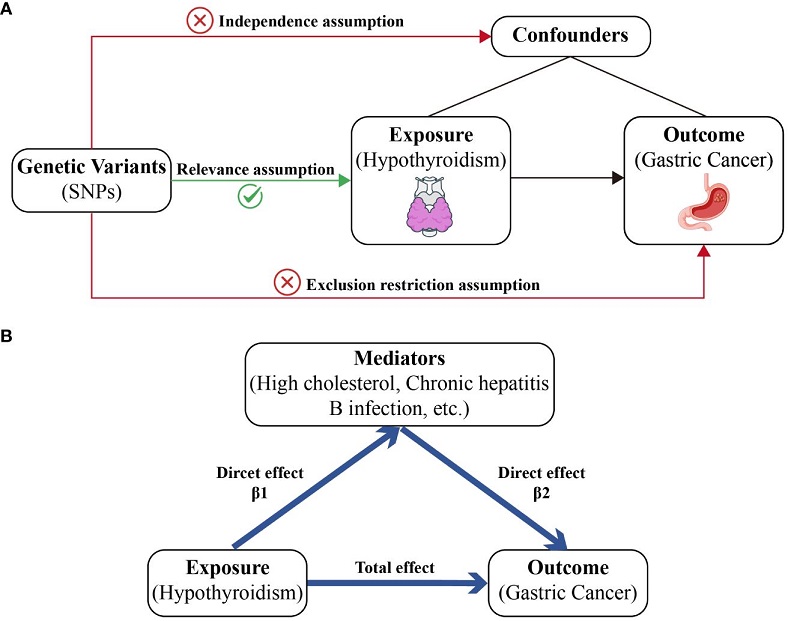
A diagram of the main Mendelian randomization (MR) study and mediator MR analysis. This diagram illustrates the potential causal pathway from hypothyroidism to GC, with high cholesterol, IBD, and SRA serving as mediators. (A) Main MR analysis. (B) Mediator MR analysis.
The Thyroid-Gastric Cancer Connection
Hypothyroidism Confers Protection Against Risk of Gastric Cancer
A diagram of the main Mendelian randomization (MR) study and mediator MR analysis. This diagram illustrates the potential causal pathway from hypothyroidism to GC, with high cholesterol, IBD, and SRA serving as mediators. (A) Main MR analysis. (B) Mediator MR analysis.
The Thyroid-Gastric Cancer Connection
Hypothyroidism, characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, affects metabolic processes and is linked to several health issues, including weight gain, depression, and hyperlipidemia. However, its potential role in cancer has been debated. Previous research indicates that thyroid hormones, which regulate numerous cellular processes, might influence cancer development. This study aimed to clarify the causal relationship between hypothyroidism and gastric cancer using Mendelian randomization (MR).
Mendelian Randomization: A Tool for Causal Inference
Mendelian randomization (MR) utilizes genetic variants as instruments to infer causal relationships between an exposure and an outcome, overcoming limitations like confounding and reverse causation commonly seen in observational studies. Genetic variants used in MR are randomly allocated at conception, mimicking the randomization process of a clinical trial. This method helps ensure that the genetic variants associated with the exposure are not confounded with other risk factors.
Study Design and Methods
The researchers conducted univariable and multivariable MR analyses using genetic variant information from the FinnGen and MRC Integrative Epidemiology Unit open genome-wide association studies (GWAS) databases. The study adjusted for confounders such as body mass index (BMI), smoking status, and alcohol intake. Additionally, mediator MR analysis examined the role of high cholesterol in the hypothyroidism-gastric cancer relationship.
Findings: Hypothyroidism's Protective Role
The study identified a significant inverse association between hypothyroidism and gastric cancer risk, with an odds ratio (OR) of 0.93. This finding suggests that hypothyroidism might confer a pro
tective effect against gastric cancer. Sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of these results, with no evidence of reverse causation or pleiotropy.
Mediators: High Cholesterol and Other Factors
Mediator analysis revealed that high cholesterol levels, chronic hepatitis B infection, and diabetes or endocrine disease status significantly mediated the protective effect of hypothyroidism on gastric cancer risk. For instance, high cholesterol alone mediated about 6.92% of the protective effect. This indicates that metabolic health and thyroid function are intricately linked to gastric cancer risk.
Mechanisms and Implications
While the protective effect of hypothyroidism against gastric cancer may seem counterintuitive, the complex interactions between thyroid hormones and various physiological processes might play a role. Thyroid hormones regulate cellular metabolism, growth, and differentiation, and their dysregulation has been implicated in several cancers. Decreased stimulation of thyroid hormone receptors in the gastrointestinal tract might inhibit cellular proliferation and oncogenic signaling pathways, potentially suppressing tumorigenesis.
High cholesterol emerged as a significant mediator. Despite hyperlipidemia's association with oxidative stress and inflammation, which are carcinogenic, studies have shown an inverse relationship between cholesterol and gastric cancer risk. This paradox suggests that the anti-inflammatory properties of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol might offer protective effects.
Diabetes and Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
Hypothyroidism's association with glucose absorption and utilization dysfunction highlights another layer of complexity. Diabetes, a mediator in the hypothyroidism-gastric cancer relationship, underscores the interplay between thyroid function, metabolic disorders, and cancer risk. Insulin resistance and dysregulated hormone signaling pathways could contribute to gastric cancer development in hypothyroid individuals.
Chronic hepatitis B infection also played a significant mediating role. Previous MR studies have shown a causal relationship between hepatitis B infection and gastric cancer. The hepatitis B virus protein X may interfere with DNA repair pathways and tumor suppressor genes, promoting tumorigenesis.
Conclusion
This groundbreaking study suggests a genetic predisposition to hypothyroidism is causally associated with a decreased risk of gastric cancer. High cholesterol, chronic hepatitis B infection, and diabetes or endocrine disease serve as significant mediators in this protective pathway. These findings offer new insights into the complex relationships between thyroid function, metabolic health, and cancer risk, highlighting potential preventive strategies and the need for further research into these associations.
Understanding these mechanisms better can pave the way for innovative preventive and therapeutic strategies for gastric cancer, particularly in individuals with hypothyroidism. As the study underscores, maintaining metabolic health and managing thyroid function could play crucial roles in mitigating gastric cancer risk, offering a new avenue for cancer prevention and control.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers in Endocrinology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/endocrinology/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024.1388608/full
For the latest about
Gastric Cancer, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/human-circular-rna-hsa-circ-0000231-can-be-used-as-a-tumor-biomarker-for-gastric-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mitochondrial-respiratory-chain-component-ndufa4-identified-as-potential-therapeutic-target-for-gastrointestinal-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/herbs-and-phytochemicals-extracts-from-rhizomes-of-atractylodes-macrocephala-koidz-baizu-can-help-in-gastric-cancer
