New study reveals how SARS-CoV-2 E protein disrupts Calcium balance by targeting SERCA
Sebastian Lavoie Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Sep 12, 2024 1 year, 5 months, 1 week, 6 hours, 44 minutes ago
Medical News: Scientists continue to unravel the complexities of how SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, affects the human body. A recent study reveals how one small viral protein, known as the envelope (E) protein, significantly disrupts calcium levels in human cells, providing fresh insights into the virus’s behavior and potential new targets for therapy. This
Medical News report highlights key findings from the research conducted by teams from Semmelweis University in Hungary, McGill University in Canada, and the Saint-Louis Research Institute in France.
 New study reveals how SARS-CoV-2 E protein disrupts Calcium balance by targeting SERCA
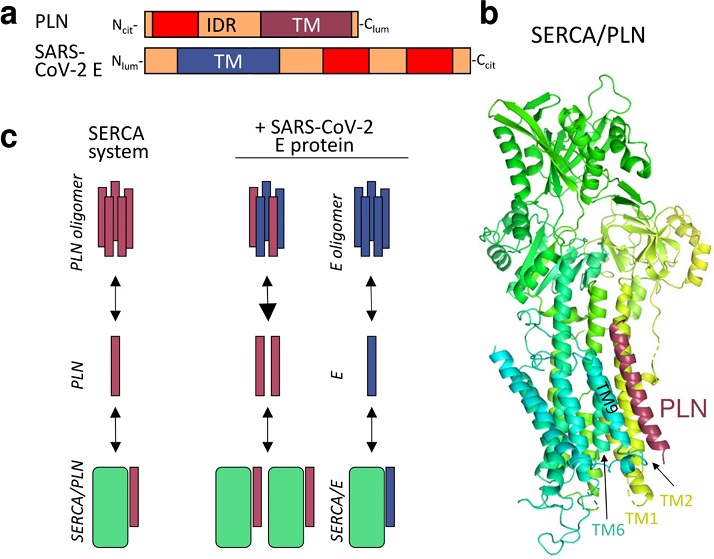
(a) Topology of PLN and E proteins. TM: transmembrane helix; IDR: intrinsically disordered region; red: potential MemMoRF. (b) The X-ray structure (PDBID: 4kyt) of the rabbit SERCA (yellow-green-turquoise)—PLN (burgundy) complex. (c) Left side shows the SERCA-PLN system. Right side depicts that E protein may interfere with the SERCA system by perturbing the PLN pentamer pool or by interacting with SERCA. burgundy: PLN; blue: E protein; green: SERCA.
New study reveals how SARS-CoV-2 E protein disrupts Calcium balance by targeting SERCA
(a) Topology of PLN and E proteins. TM: transmembrane helix; IDR: intrinsically disordered region; red: potential MemMoRF. (b) The X-ray structure (PDBID: 4kyt) of the rabbit SERCA (yellow-green-turquoise)—PLN (burgundy) complex. (c) Left side shows the SERCA-PLN system. Right side depicts that E protein may interfere with the SERCA system by perturbing the PLN pentamer pool or by interacting with SERCA. burgundy: PLN; blue: E protein; green: SERCA.
The SARS-CoV-2 E protein is a structural component of the virus and is highly expressed in infected cells. Researchers already knew that this protein played a vital role in viral replication, but its specific function in cells remained largely unknown. Scientists have now identified how the E protein interferes with SERCA, an important enzyme that manages calcium flow within cells.
The Role of Calcium in Cells
Calcium isn’t just important for strong bones - it plays a crucial role inside cells, acting as a signaling molecule that helps regulate processes like muscle contraction, cell growth, and even cell death. Maintaining proper calcium levels within different parts of the cell is essential for normal function. SERCA enzymes help move calcium from the cell’s cytoplasm into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), an important cell compartment responsible for producing and processing proteins.
The new study focused on how the SARS-CoV-2 E protein affects SERCA, and the findings are groundbreaking. Researchers discovered that the E protein alters the activity of SERCA, disrupting the normal flow of calcium within cells.
How SARS-CoV-2 E Protein Interferes with SERCA
Using advanced lab techniques like FRET (Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer), scientists found that the SARS-CoV-2 E protein can form clusters (called oligomers) with SERCA and other cellular proteins known as regulins, which typically control SERCA activity. The E protein behaves similarly to a natural regulator of SERCA, but instead of fine-tuning calcium levels, it causes disruptions.
In their experiments, the researchers observed that the E protein binds to SERCA, directly reducing its ability to pump calcium back into the ER. This leads to calcium imbalances inside the cell, which can contribute to severe inflammation a
nd cellular dysfunction. The study also used structural modeling techniques to show exactly how the E protein and SERCA interact. The overlapping interaction sites between the viral protein and endogenous regulins suggest that the E protein competes with normal cellular regulators for control over calcium management.
Implications for COVID-19 Treatment
This discovery offers new hope for better treatment options for severe COVID-19 cases. By understanding how the E protein alters calcium signaling, scientists may be able to design drugs that target this interaction, potentially reducing the damage caused by the virus. For example, by preventing the E protein from interfering with SERCA, it might be possible to restore normal calcium balance in cells, which could help manage the extreme inflammation seen in severe COVID-19 cases.
The research also opens up new avenues for therapeutic intervention. SERCA plays a key role in many vital cellular processes, including those in the lungs and heart. The disruption of calcium levels by the SARS-CoV-2 E protein may help explain why COVID-19 has such a wide-ranging impact on different organs.
Study Findings in Detail
The study, conducted in a laboratory setting, used human cells to observe the interactions between the E protein and SERCA. By labeling the E protein and SERCA with fluorescent markers, researchers were able to see how these proteins interacted within the cells. The findings showed that cells expressing the SARS-CoV-2 E protein had much lower levels of calcium within the ER compared to control cells without the viral protein. These lower calcium levels indicate that SERCA’s function was severely compromised by the presence of the E protein.
Additionally, the study showed that the E protein caused a "switch-like" response in calcium levels when cells were stimulated with ATP, a molecule that normally triggers calcium release from the ER. In normal cells, the calcium levels dropped gradually, but in cells with the E protein, the calcium levels plummeted rapidly. This rapid depletion of calcium stores suggests that the E protein makes cells more susceptible to calcium imbalances, which can lead to severe cell stress and inflammation.
Conclusion: A New Pathway for COVID-19 Therapies
The discovery that the SARS-CoV-2 E protein disrupts calcium signaling in cells offers a fresh perspective on how the virus wreaks havoc in the human body. This research could pave the way for new treatments that specifically target this viral protein, reducing the damage caused by calcium imbalances and inflammation.
By focusing on the interaction between the E protein and SERCA, scientists have identified a potential therapeutic target that could mitigate some of the most severe symptoms of COVID-19. As researchers continue to explore these findings, the hope is that they will lead to more effective treatments for patients suffering from this deadly virus.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Scientific Reports.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1038/s41598-024-71144-5
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-e-protein-triggers-neuron-cell-death-via-calcium-release
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-study-shows-that-covid-19-causes-changes-in-phosphocalcium-metabolism
