Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 20, 2024 1 year, 8 months, 2 weeks, 5 days, 11 hours, 27 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: As the world battles the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the scientific community continues to search for innovative and effective treatments. Among the many potential solutions, an unexpected contender has emerged: milk proteins. These natural defenders have shown remarkable antiviral properties, particularly against SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. This
COVID-19 News report delves into a new study review by researcher from the University of Maryland Eastern Shore-USA, Department of Animal Husbandry Amritsar-India and Guru Angad Dev Veterinary and Animal Sciences University-India that explored the fascinating potential of milk proteins and their derived peptides in combating this global health crisis.
 Milk Proteins And Peptides Could Help Fight COVID-19
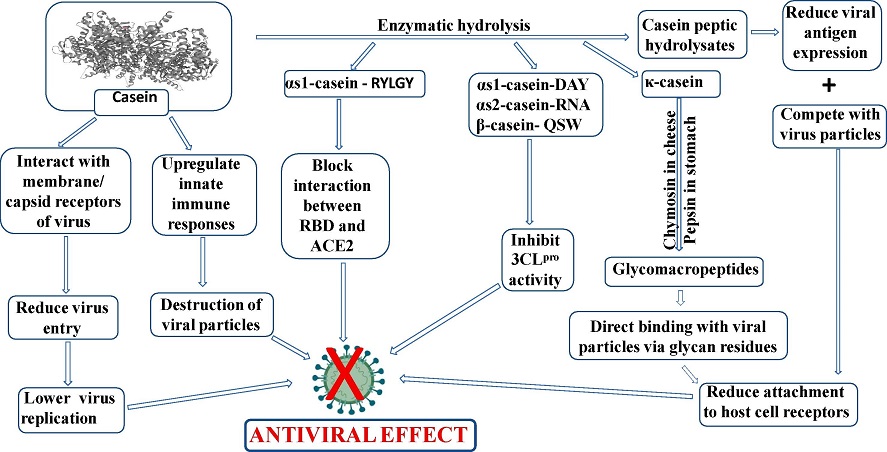
A summarized schematic representation of different pathways by which casein and casein-related peptides exert antiviral effects both by acting against the viral particles and for the host cell
The Pandemic's Challenge and the Search for Natural Solutions
Milk Proteins And Peptides Could Help Fight COVID-19
A summarized schematic representation of different pathways by which casein and casein-related peptides exert antiviral effects both by acting against the viral particles and for the host cell
The Pandemic's Challenge and the Search for Natural Solutions
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the highly contagious SARS-CoV-2, has reshaped our world. With its primary mode of transmission through respiratory droplets, the virus spreads rapidly, necessitating urgent and effective interventions. One of the major hurdles in controlling the virus is its ability to mutate quickly, leading to new variants that can evade vaccines and other pharmaceutical measures. This ongoing evolution of the virus underscores the need for innovative treatment approaches.
Amid this challenge, natural antivirals have gained attention for their potential to complement existing treatments. Unlike chemical antivirals, natural antivirals often have fewer side effects and are more broadly accepted by the public. Functional foods, particularly those rich in bioactive proteins and peptides, have emerged as promising candidates. Among these, milk proteins stand out for their impressive antiviral properties.
Milk Proteins: Nature's Defense Mechanism
Milk, a staple in many diets, is more than just a source of nutrition. It contains a wealth of bioactive proteins and peptides that offer various health benefits, including potent antiviral properties. These proteins and peptides can interfere with the viral replication cycle at multiple stages, from entry to post-processing. Notably, bovine lactoferrin, a prominent milk protein, has been reported to enhance the effects of remdesivir, an FDA-approved anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug.
Casein: The Powerhouse Protein
Beyond its nutritional value, casein has shown significant antiviral potential. Studies have indicated that enzymatically hydrolyzed casein peptides can inhibit viral replication by interacting with viral proteins and receptors. This dual role of casein as both a nutrient and an antiviral agent highlights its potential in the fight against COVID-19.
;
Casein, which makes up about 80% of the total protein content in bovine milk, is a powerhouse when it comes to antiviral activity. This protein, and its derived peptides, have shown efficacy against several viruses, including influenza and HIV. Recent studies have highlighted casein's potential to inhibit the entry and replication of SARS-CoV-2. For example, research has demonstrated that casein from goat milk can prevent the virus from entering host cells by interacting with viral receptors, thereby blocking its replication.
Enzymatic hydrolysis of casein generates peptides with a range of bioactivities, including antioxidant and antihypertensive properties. These peptides have also shown potential antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in various studies, suggesting their promise as natural antiviral agents.
Whey Proteins: More Than Just a Supplement
Whey proteins, constituting about 20% of the protein content in bovine milk, also boast significant antiviral properties. This group includes α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin, lactoferrin, lysozyme, and lactoperoxidase.
Lactoferrin: The Multifaceted Defender
Lactoferrin is a multifunctional whey protein renowned for its broad-spectrum antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Extensive research has focused on lactoferrin's potential against SARS-CoV-2. Studies have shown that lactoferrin can inhibit the virus by binding to host cell surface molecules and viral receptors, preventing viral attachment and internalization.
Both human and bovine lactoferrin have demonstrated significant antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Notably, bovine lactoferrin has shown higher efficacy compared to its human counterpart, effectively inhibiting the virus's replication by inducing interferon responses and blocking viral attachment.
Lactoferrin's multifunctional properties make it a standout candidate for antiviral therapy. Its ability to enhance the body's immune response, coupled with its direct antiviral effects, positions lactoferrin as a potent natural remedy against SARS-CoV-2. Clinical trials have shown that lactoferrin can significantly reduce viral load and improve recovery times in COVID-19 patients.
α-Lactalbumin and β-Lactoglobulin: Dual Antiviral Agents
These two major whey proteins have also shown impressive antiviral activities. α-Lactalbumin can inhibit the virus's entry by interfering with viral attachment and entry processes. β-Lactoglobulin, on the other hand, has been found to inhibit cathepsin L, a protease crucial for SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells, thereby preventing infection.
Lactoperoxidase: The Enzyme with a Punch
Lactoperoxidase, another whey protein, has proven antiviral activities against a variety of viruses. Its antiviral action is attributed to the production of reactive intermediates that possess potent virucidal properties. Studies have shown that lactoperoxidase can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication by blocking viral attachment and preventing the formation and assembly of viral proteins.
Milk Fat Globule Membrane Proteins: A Unique Defense System
Milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) proteins, such as mucins and lactadherins, add another layer of defense. Mucins, heavily glycosylated proteins, act as decoy proteins to prevent viruses from binding to host cells. Lactadherin, another MFGM protein, can inactivate viruses and reduce inflammation by enhancing the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells.
The Role of Glycosylation in Antiviral Activity
Glycosylation, a post-translational modification of milk proteins, plays a crucial role in their antiviral activity. Glycosylated milk proteins can competitively bind to viral receptors, preventing viruses from attaching to host cells. Studies have shown that glycosylated proteins from bovine milk can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication by blocking the interaction between the virus's spike protein and ACE2 receptors on host cells.
Harnessing the Power of Milk Proteins
The potential of milk proteins and peptides as natural antiviral agents against SARS-CoV-2 is immense. These bioactive components can act at various stages of the viral replication cycle, making them promising candidates for developing new antiviral treatments. However, while the initial findings are promising, further validation through in vivo studies and clinical trials is essential to determine their efficacy, safety, and optimal dosages.
Future Directions: Expanding the Horizon
The exploration of milk proteins and peptides as antiviral agents opens up exciting possibilities for natural and safe antiviral treatments. While the current focus is on SARS-CoV-2, these bioactive components could potentially be effective against other viral infections.
Integrating Milk Proteins into Treatment Protocols
Given their safety profile and natural occurrence, milk proteins and peptides could be integrated into existing treatment protocols for COVID-19. This approach could enhance the effectiveness of current therapies and provide a natural complement to pharmaceutical interventions.
Conclusion: Embracing Nature's Remedies
In the quest to combat COVID-19, milk proteins and peptides offer a promising and natural solution. Their ability to interfere with the viral replication cycle at multiple stages makes them valuable allies in the fight against this global pandemic. As research continues, these natural defenders may well become a cornerstone of our antiviral arsenal, providing safe, affordable, and effective treatments for COVID-19 and beyond.
The journey of milk proteins from the dairy aisle to the frontlines of antiviral research is a testament to the power of nature's remedies. As we continue to explore their potential, one thing is clear: the future of antiviral therapy may very well be found in a glass of milk.
The study review was published in the peer reviewed Journal of Functional Foods.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464624002391
For more about
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-vitro-study-involving-vero-cells-shows-that-whey-protein-especially-from-human-breast-milk-inhibits-sars-cov-2-coronavirus
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/lactoferrin-an-iron-binding-protein-with-antiviral-and-antibacterial-properties
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-infected-children-show-persisting-gastrointestinal-symptoms-over-18-months-lactoferrin-helps
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/numerous-studies-are-showing-that-lactoferrin-can-be-used-as-an-adjuvant-in-covid-19-treatment-protocols
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-scientists-find-that-the-otc-drug-diphenhydramine-when-paired-with-lactoferrin-could-be-a-new-therapeutic-for-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/must-read-immune-system-natural-protein-found-in-mother-s-milk-and-colostrum-called-lactoferrin-could-help-protect-against-various-viruses
