COVID-19 News: Study Shows That SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Is A Modulator Of Cytokine Induction
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jan 23, 2024 2 years, 2 weeks, 6 days, 12 hours, 4 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The ongoing global battle against the COVID-19 pandemic has spurred relentless research efforts to comprehend the intricacies of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and its impact on the human immune system. A recent study conducted by researchers from the Universidade Federal do ABC (UFABC) in São Paulo, Brazil, in collaboration with Cambridge University and the University of St Andrews in the UK, has shed light on a crucial aspect of the virus's interaction with the immune response. The study reveals that the SARS-CoV-2 accessory protein, ORF8, plays a pivotal role in modulating cytokine responses, particularly those linked to type I interferon (IFN) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). In this
COVID-19 News report, we delve into the multifaceted functions of ORF8, exploring its structural characteristics, evolutionary origins, and its impact on both innate and adaptive immunity.
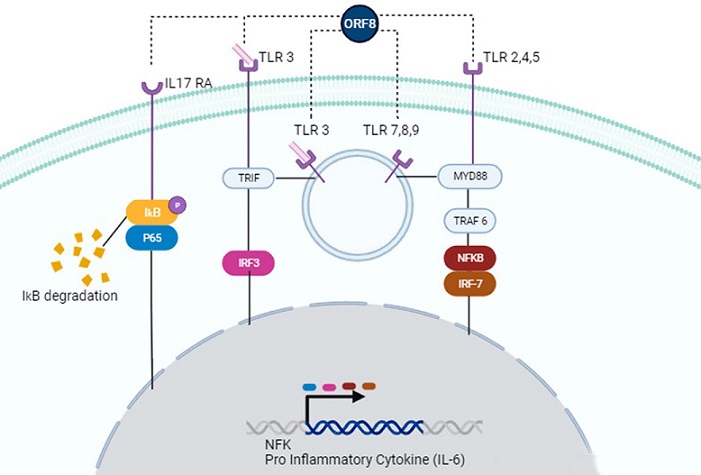 Possible signaling pathways activated by ORF8. ORF8 accessory protein can act through IL-17 RA (left), TLR 3 (left, center), TLR 7,8,9 (center), or TLR 2,4,5 (right). In the IL-17 RA cascade, ORF8 leads to IkB/P65 phosphorylation, causing degradation of IκΒα and subsequent activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Recognition of ORF8 by TLRs activates TRIF and/or MyD88 pathways, enhancing gene transcription of NF-κB genes or pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6.
Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Immune Response
Possible signaling pathways activated by ORF8. ORF8 accessory protein can act through IL-17 RA (left), TLR 3 (left, center), TLR 7,8,9 (center), or TLR 2,4,5 (right). In the IL-17 RA cascade, ORF8 leads to IkB/P65 phosphorylation, causing degradation of IκΒα and subsequent activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Recognition of ORF8 by TLRs activates TRIF and/or MyD88 pathways, enhancing gene transcription of NF-κB genes or pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6.
Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Immune Response
Severe cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection are marked by an overactive immune response, resulting in the release of excessive pro-inflammatory cytokines. This cytokine storm contributes to various complications, including lung damage, cardiovascular symptoms, hematologic issues, acute kidney injury, and, in extreme cases, multiple organ failure leading to death. The primary culprits behind this heightened cytokine production are viral proteins, with particular attention drawn to the unique accessory protein, ORF8.
Overview of SARS-CoV-2 Genome and ORF8
The SARS-CoV-2 genome comprises 14 open reading frames (ORFs), including ORF8, which is distinct to SARS-CoV-2. Although poorly conserved among other human coronaviruses, ORF8 shares a significant amino acid sequence similarity with Bat-RaTG13-CoV, suggesting a potential origin from bats. Notably, ORF8 exhibits high susceptibility to mutations, with the L84S variant being prevalent in the early months of the pandemic. This mutation has been linked to milder disease outcomes, indicating that ORF8 serves as a virulence factor.
Structural and Evolutionary Insights into ORF8
Structural analysis of ORF8 reveals its unique characteristics, including four pairs of disulfide bonds and glycosylation at residue N78, essential for stabilizing its structure. ORF8 is abundantly secreted, making it highly immunogenic. Despite being classified as an accessory protein, ORF8 has the largest protein interactome network among SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins. Various studies have unveiled its biological properties, encompassing immune evasion and activation of signaling pathways.
<
strong>ORF8 as a Modulator of Cytokine Responses
The study conducted by UFABC, Cambridge University, and the University of St Andrews delves into the role of ORF8 as a modulator of cytokine responses, particularly focusing on its impact on type I interferon (IFN) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Investigations indicate that ORF8 augments IL-6 production induced by Poly(I:C) in human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cells and monocyte-derived dendritic cells (mono-DCs). The study hypothesizes that ORF8 may act through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs).
Cytokine Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Immune Dysregulation
Severe cases of COVID-19 are associated with a cytokine storm, characterized by excessive circulating cytokine levels, endothelial damage, vascular permeability, coagulopathy, and immune cell infiltration, ultimately leading to multi-organ failure. Individuals with certain risk factors, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and advanced age, are more susceptible to an inappropriate immune response, resulting in severe outcomes. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 infection in pediatric patients can lead to multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS), emphasizing the broad impact of the virus on various age groups.
Innate Antiviral Immunity and Adaptive Immune Responses
Innate antiviral immunity is triggered by the recognition of viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) via pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Type I interferons play a crucial role in inhibiting viral replication and regulating adaptive immune responses. Adaptive immune responses, including CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, work to control viral infections. Failure to mount an adequate adaptive response can lead to a continuous cytokine storm, causing multi-organ infection and potential organ failure.
SARS-CoV-2 Antagonism of the Immune System
SARS-CoV-2 employs various mechanisms to evade both innate and adaptive immune responses. Several viral proteins, including Nsp1, Nsp3, Nsp12, Nsp13, Nsp14, Nsp15, M, N, S, ORF3b, ORF6, and ORF8, antagonize type I interferon induction and signaling pathways. The virus also evolves strategies to combat T cell activation, such as acquiring mutations that reduce T cell recognition. ORF8, in particular, interacts with the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I), inhibiting T cell-mediated lysis of infected cells.
ORF8 as a Type I IFN Antagonist
Research conducted by the UFABC-led team reveals that ORF8, especially the L84S variant, inhibits IFN-β in HEK-293 cells but can augment type I IFN-β expression in mono-DCs. The mechanism involves the deamidation of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and interference with the IFN-β signaling pathway. Additionally, ORF8 induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, activating the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
ORF8 as a Pro-Inflammatory Virokine
Apart from its role in immune evasion, ORF8 has been implicated as a pro-inflammatory virokine, inducing inflammatory responses. Interactome analyses indicate its interaction with TGF-β1-LTBP1 complex and the PRR NLRP3, contributing to cytokine responses. ORF8 mimics the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-17, activating downstream inflammatory pathways, including NF-κB signaling. However, the precise mechanisms and conditions under which ORF8 induces inflammation remain to be fully elucidated.
ORF8 as a Potential Cytokine Modulator through TLRs
Recent studies challenge previous findings, suggesting that ORF8 signaling in myeloid cells depends on the TLR/IL-1 family adaptor MyD88 and the TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF). This implies that ORF8 might activate TLRs, especially those recognizing dsRNA, such as TLR3. The implications of ORF8-mediated TLR activation on the overall immune response and cytokine modulation warrant further investigation.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The study by UFABC, Cambridge University, and the University of St Andrews provides valuable insights into the intricate interplay between SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 and the immune response. Understanding the multifaceted functions of ORF8, ranging from immune evasion to cytokine modulation, is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic strategies. Future research endeavors should explore the impact of ORF8 on different cell types, assess its role in the context of viral evolution, and elucidate the precise signaling pathways through which it exerts its effects. Ultimately, unraveling the complexities of ORF8 function will contribute to the development of more effective treatments for COVID-19 and enhance our preparedness for future viral threats.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Viruses.
https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/16/1/161
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-oligomer-formation-of-sars-cov-2-orf8-through-73yidi76-motifs-regulates-immune-response-and-non-infusion-antiviral-interactions
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-orf8-forms-intracellular-aggregates,-inhibiting-ifn-induced-antiviral-gene-expression-in-lung-epithelial-cells
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-news-scientist-from-india-find-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-possesses-complement-inhibitory-properties
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-accessory-proteins-orf6,-orf8,-orf9b,-orf9c-have-the-ability-to-trigger-inflammatory-and-profibrotic-processes-through-il11-signaling
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/u-s-study-reveals-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-triggers-inflammatory-response-in-immune-cells-through-myd88-independently-of-the-il-17-receptor
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/unique-sites-of-immune-regulation-discovered-in-sars-cov-2-orf8
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-sublineages-lacking-orf8-protein-do-not-replicate-in-upper-respiratory-tract,-reducing-transmission-but-increasing-inflammation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-validates-that-sars-cov-2-accessory-proteins-orf6,-orf8,-orf9b-and-orf9c-involved-in-profibrotic-processes
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-orf8-protein-of-sars-cov-2-induces-endoplasmic-reticulum-stress-like-responses-and-facilitates-virus-replication-by-triggering-calnexin
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-exhibits-complement-inhibitory-properties-and-damages-innate-immunity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-yale-study-shows-that-omicron-subvariants-are-evolving-further-through-mutations-on-orf8-proteins-to-escape-from-mhc-i-recognition
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-french-scientists-uncover-how-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-causes-dysregulation-of-gene-expression-in-infected-cells
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/university-of-pennsylvania-study-finds-that-sars-cov-2-uses-histone-mimicry-to-disrupt-host-epigenetic-regulation-for-disarming-host-immune-responses
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mayo-clinic-researchers-discover-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-is-the-key-factor-that-is-causing-covid-19-disease-severity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-encoded-protein-contains-a-histone-mimic-that-disrupts-human-host-cell-epigenetic-regulation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-university-of-california-scientist-identify-rapidly-evolving-immune-evasion-protein-sars-cov-2-orf8-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-briefs-anti-androgens-and-covid-19,-possible-cytotoxic-t-cell-therapy-for-covid-19,-immune-evasion-by-evolving-orf8-protein-in-sars-
