COVID-19 Herbs: Study Finds That Galangal-Cinnamon Spice Mixture Blocks Coronavirus Infection Pathway Through Inhibition Of SARS-CoV-2 MPro!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Sep 30, 2023 2 years, 4 months, 3 weeks, 20 hours, 48 minutes ago
COVID-19 Herbs: The COVID-19 pandemic has swept across the globe, leaving a trail of illness and death in its wake. With millions infected and thousands losing their lives, the search for effective treatments and preventive measures has become paramount. While vaccines offer some hope, the need for affordable and readily available treatments for those afflicted with mild to moderate cases of the virus remains essential. In this pursuit, researchers are turning to natural remedies, such as herbs and spices, to uncover potential solutions. One such promising combination is the galangal-cinnamon spice mixture, which recent studies have found to possess the ability to block the coronavirus infection pathway by inhibiting the SARS-CoV-2 MPro enzyme.
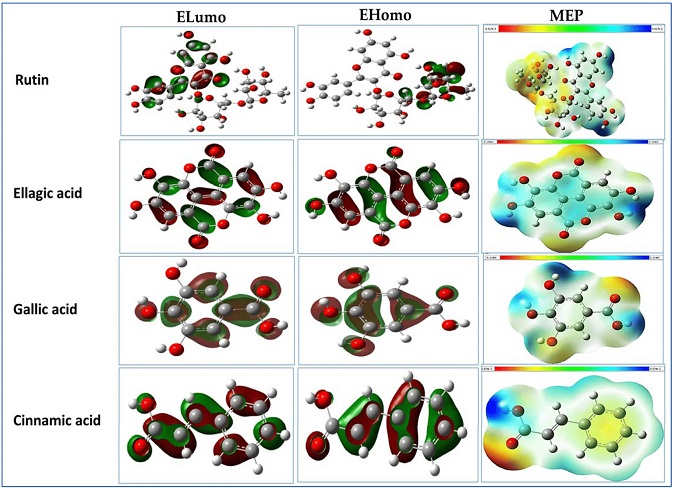 Frontier molecular orbitals (HOMOs, LUMOs) and molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) surface of the rutin, ellagic, gallic, and cinnamic acids by using the DFT/B3LYP/6-311++G(2d,2p) method.
Frontier molecular orbitals (HOMOs, LUMOs) and molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) surface of the rutin, ellagic, gallic, and cinnamic acids by using the DFT/B3LYP/6-311++G(2d,2p) method.
A new
COVID-19 Herbs study by researchers from Helwan University-Egypt, Beni-Suef University Hospitals and Beni-Suef University-Egypt, Nahda University (NUB)-Egypt, King Khalid University-Saudi Arabia, Zewail City of Science and Technology-Egypt, El Saleheya El Gadida University-Egypt, Jouf University-Saudi Arabia and Al-Azhar University-Egypt sheds light on the potential of this herbal remedy in the fight against COVID-19.
The Role of Natural Products in COVID-19 Treatment
Amid the ongoing COVID-19 crisis, the search for effective treatments and preventatives has led researchers to explore the potential of natural products, particularly herbs and spices. These readily accessible and cost-effective resources have garnered attention for their ability to complement existing treatment protocols for mild and moderate COVID-19 cases. Rich in secondary metabolites such as polyphenols, flavonoids, tannins, alkaloids, and terpenoids, these natural remedies offer anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and antimicrobial properties, making them attractive candidates for inclusion in treatment strategies.
As the demand for herbal remedies, particularly in the form of convenient tea bags, continues to rise, researchers are exploring their efficacy in mitigating the impact of COVID-19. Not only do these herbal drinks provide potential health benefits, but they also offer a tasty and appealing means of consumption. In this context, the galangal-cinnamon mixture emerges as a promising candidate, given its antiviral potential against coronaviruses and the presence of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, essential oils, and terpenoids.
Understanding the Study
The collaborative research team embarked on a journey to evaluate the inhibitory effects of a galangal-cinnamon aqueous extract (GCAE) against the Low Pathogenic Human Coronavirus HCoV-229E. This choice of virus was deliberate, as it presents a safer option for in vitro laboratory experimentation. Furthermore, the structural and binding similarities between HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 MPro made it a suitable surrogate for assessing the potential antiviral properties of GCAE.
<
;strong>Key Findings
The study yielded significant results, showcasing the potent antiviral activity of the GCAE. The extract exhibited an impressive half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 15.083 µg/mL, indicating its ability to inhibit the replication of HCoV-229E. To put this in perspective, GCAE's antiviral potency was nearly half that of remdesivir, a standard antiviral drug with broad-spectrum activity against the coronavirus family.
The chemical composition of the GCAE was further elucidated through high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-ultraviolet (HPLC-DAD-UV) analysis. This analysis identified twelve phenolic compounds within the extract, with ellagic, cinnamic, and gallic acids emerging as the major phenolic acids. Additionally, rutin was identified as the predominant flavonoid glycoside.
It's worth noting that while these compounds were present in the GCAE, they were not detected in the individual galangal or cinnamon extracts. This suggests that the unique combination of these herbs, as well as potential interactions during the mixture preparation, may be responsible for these findings.
Quantum Chemical Calculations: Bridging Theory and Experimentation
To gain deeper insights into the molecular properties of the identified phenolic compounds, the study team turned to quantum-chemical calculations. Employing the Density Functional Theory (DFT) with the B3LYP method and a 6-311++G(2d,2p) basis set, they explored critical parameters such as EHOMO, ELUMO, energy gap, ionization potential, chemical hardness, softness, and electronegativity values. These calculations provided valuable data that enhanced the understanding of the compounds' behavior and potential interactions.
The Quantum-Molecular Docking Approach
Taking their investigation, a step further, the research team conducted molecular docking studies to predict the specific targets of the phenolic compounds within the GCAE. Virtual screening was employed to identify potential interactions with three key targets of HCoV-229E: the main protease (MPro), spike glycoprotein, and receptor-binding domain (RBD). Among the compounds analyzed, rutin emerged as the primary component responsible for inhibiting these crucial targets. Importantly, these targets play a pivotal role in the entry and replication of SARS-CoV-2, making rutin a promising candidate for further study.
Potential Health Benefits Beyond Antiviral Activity
Beyond their antiviral properties, phenolic compounds found in medicinal plants like those in GCAE offer a range of health benefits. Ellagic acid, for instance, boasts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, potentially aiding in the recovery of COVID-19 patients.
Cinnamic acid, with its ability to modulate inflammatory cytokines and decrease TNF-α in serum, holds promise as an immune-modulating agent. Gallic acid, known for its strong free radical-scavenging activities, anti-inflammatory properties, and immunomodulatory effects, could prove valuable in bolstering the immune response of patients.
Furthermore, rutin has demonstrated immune-regulatory effects, influencing cytokine levels and immune-related signaling pathways. This could lead to an enhancement in antibody levels, increased immunoglobulin levels, and the restoration of leucocyte function.
Conclusion
In the ongoing battle against COVID-19, the search for effective treatments and preventatives remains a top priority. Natural products like the galangal-cinnamon spice mixture are emerging as promising candidates due to their potential antiviral properties and numerous health benefits. The collaborative research effort presented in this study has shed light on the inhibitory effects of GCAE against HCoV-229E, highlighting rutin as a key player in blocking essential targets for coronavirus entry and replication.
As the world continues to grapple with the pandemic, harnessing the power of nature through rigorous scientific inquiry offers hope for a brighter future. The galangal-cinnamon spice mixture, enriched with phenolic compounds, stands as a testament to the potential of herbal remedies in the fight against COVID-19 and other viral diseases. Further research and clinical trials are warranted to validate these findings and pave the way for effective treatments and preventatives derived from natural sources, providing an affordable and accessible arsenal against the virus.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Pharmaceuticals.
https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/16/10/1378
For the latest on
COVID-19 Herbs, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/italian-study-finds-cinnamaldehyde-is-an-effective-adjuvant-therapeutic-compound-for-reducing-inflammation-in-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-herbs-german-american-study-shows-that-cinnamaldehyde-from-cinnamon-is-a-good-supplement-with-dexamethasone-for-treating-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/cinnamon-the-natural-remedy-for-flu-infections-and-beyond
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/must-read-covid-19-supplements-could-rutin-be-the-secret-ingredient-in-china%E2%80%99s-tcm-formulations-that-helped-treat-covid-19-as-adjuvant-protocols
